Guide to printers and MFPs: printing technologies, CISS, photo printing, portable printers

One of the most important points in the program when choosing a printer or MFP is the printing technology used. It determines the scope of application of printing equipment and its suitability for certain tasks.
Common Printing Technologies
1. Inkjet printing
The destiny of inkjet printers and MFPs is home use and light office workloads. Advanced copies of “ink jets” are used in design agencies, photo studios, and when creating large-format advertising products.
With inkjet technology, the image is applied to paper using microscopic drops of ink directed by the print head. Equipment of this kind must work without long downtime, since after a pause of several days, the remaining ink in the head dries out, deteriorating the print quality. The technology successfully implements high quality and resolution of color printing at a resolution of up to 9600x2400 dpi, and is well suited for printing photographs at home.
 |
| Diagram of a conventional inkjet printer. |
Modern inkjet models most often use a four-color CMYK scheme. It consists of blue (Cyan), magenta (Magenta), yellow (Yellow) and black colors (Key Color). Color ink is usually combined in one three-color cartridge, black ink is concentrated in a separate one. For professional-level photo printing, six-, nine-, and twelve-color devices are available, but they are not cheap and not everyone needs them. We will talk separately about the caste of models with built-in CISS below.
Inkjet printers and MFPs are suitable for relatively small volumes of black-and-white printing and high-quality color prints. They are inferior to the next category of equipment in terms of printing speed, the cost of obtaining one print and the short shelf life of the ink.
2. Laser printing
Laser technology is widely used for printing large volumes of text documents. The overwhelming majority of “laser printers” are made in monochrome; they are more expensive than inkjet printers and MFPs, but they are many times faster and provide a lower cost of obtaining one print.
The meaning of the technology comes down to printing with a laser beam: it marks individual areas of the photosensitive drum, powdered ink sticks to these areas, which is then transferred to paper. To fix the image, the sheet passes through a system of rollers, where the paper is heated and molten toner particles are imprinted into its surface. Prints on paper are resistant to water and sunlight, and laser printers can easily withstand long periods of downtime. The toner for them does not have an expiration date. Such devices are suitable for those who have to print a lot and often.
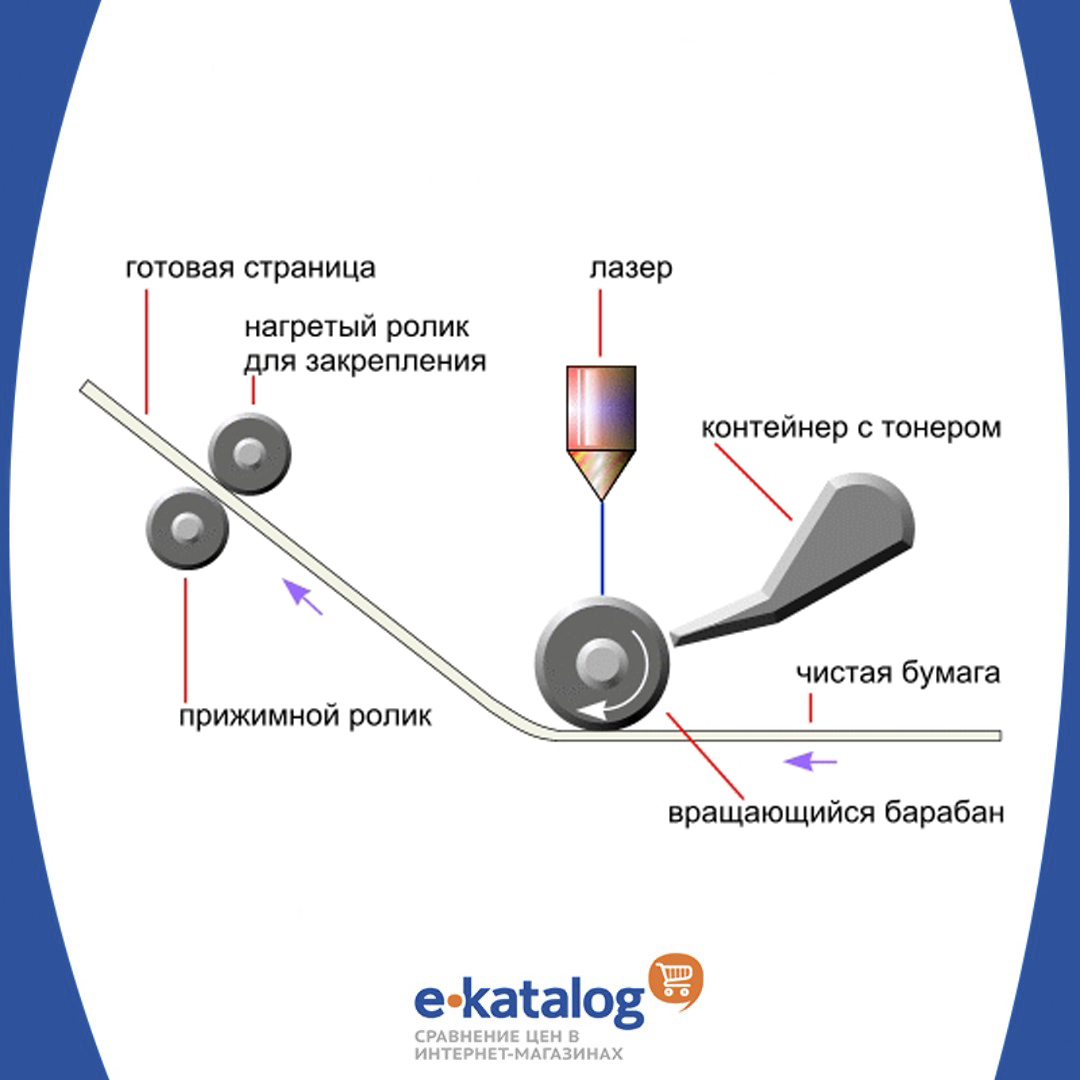 |
| A visual principle of operation of laser printers and MFPs. |
Photos from color laser printers and MFPs don't turn out very well. Laser technology is also larger, consumes more electricity and is more expensive than inkjet counterparts. Another flaw of “laser machines” is the inevitable formation of ozone during operation of the device (in high concentrations it can harm the human body).
3. LED printing
LED printing technology is a close relative of laser printing. Only instead of a laser beam, it uses an array of LEDs coupled with focusing lenses to form an image. The light source hits the shaft that is sensitive to it, the charge changes in the illuminated parts of the drum and the coloring powder is attracted to them. LED printers and MFPs are adapted for printing large volumes of text documents and graphic materials, but at the same time, such equipment is not best suited for printing photographs.
 |
| LED printing devices are similar in the principle of obtaining prints to laser printers. |
LED printing devices are cheaper than laser printers, are characterized by almost silent operation, and are less likely to fail. The same powder toner is used as ink. LED printers are cheaper than their laser counterparts, and their dimensions are often smaller, which is beneficial for models of this format only for future use.
4. Sublimation printing
Unlike the above , sublimation technology is used in portable form factor photo printers. It is designed for printing photographs in “camping” conditions. Sublimation printers contain a dye film and a heating element inside. When the paper passes between them, the paint literally “eats” into the pores of the sheet, and a special protective coating is applied on top.
 |
| Sublimation printing technology is the basis of almost all portable photo printers. |
The technology makes it possible to achieve high-quality color rendering and a very small size of one dot. The other side of the coin is the high cost of consumables for such printers and the slowness of the printing process. Plus, prints are sensitive to ultraviolet rays.
Printer-scanner-copier
Printing documents and photographs is the main, but by no means the only task of printing equipment. Multifunctional devices (MFPs) combine the functions of a printer, scanner and copier in one bottle. And some models have a telephone and a fax machine in addition.
 |
| Using an MFP you can print, photocopy and scan documents. |
MFPs are often not much more expensive than printers with similar characteristics, use the same printing technologies, and impress with their versatility of use. For office “registration” with a solid document flow , “3-in-1” laser devices are suitable, for the home - compact inkjet MFPs with the ability to print high-quality photographs. Office workers will appreciate the armada of additional options on board the MFP: A3 printing, auto-feeding of originals, two-sided printing, duplex copying, etc.
Continuous Ink Supply Systems (CISS)
The high cost of consumables for inkjet printers and MFPs is a stumbling block to the success of this printing technology. CISS - continuous ink supply systems - served as a salvation from huge financial expenses for replacing cartridges for inkjet printers.
The first CISS were handmade by folk craftsmen. Syringes were used to replace the original cartridges, paint jars, and dropper tubes for ink supply. As a complement to the design, emulators of the original cartridge chips were used (so that the printer “sees” them and does not “fall” into an accident). Of course, such systems required constant adjustment and were very difficult to operate. And their connection to the printer rarely occurred without interference in the design of the equipment and entailed loss of warranty.
 |
| Homemade CISS were often made from readily available materials. |
CISS reached a new qualitative level with the advent of factory-made paint capsules. The original systems consist of ink tanks, a cable for delivering ink to the cartridges, and the cartridges themselves, which replicate the factory ones and are installed in their place. The advantages of CISS include:
- significant reduction in the cost of a print;
- the ability to establish uninterrupted large-volume printing;
- increasing the productivity of inkjet printers and MFPs in general;
- easy refilling of tanks with the required ink color.
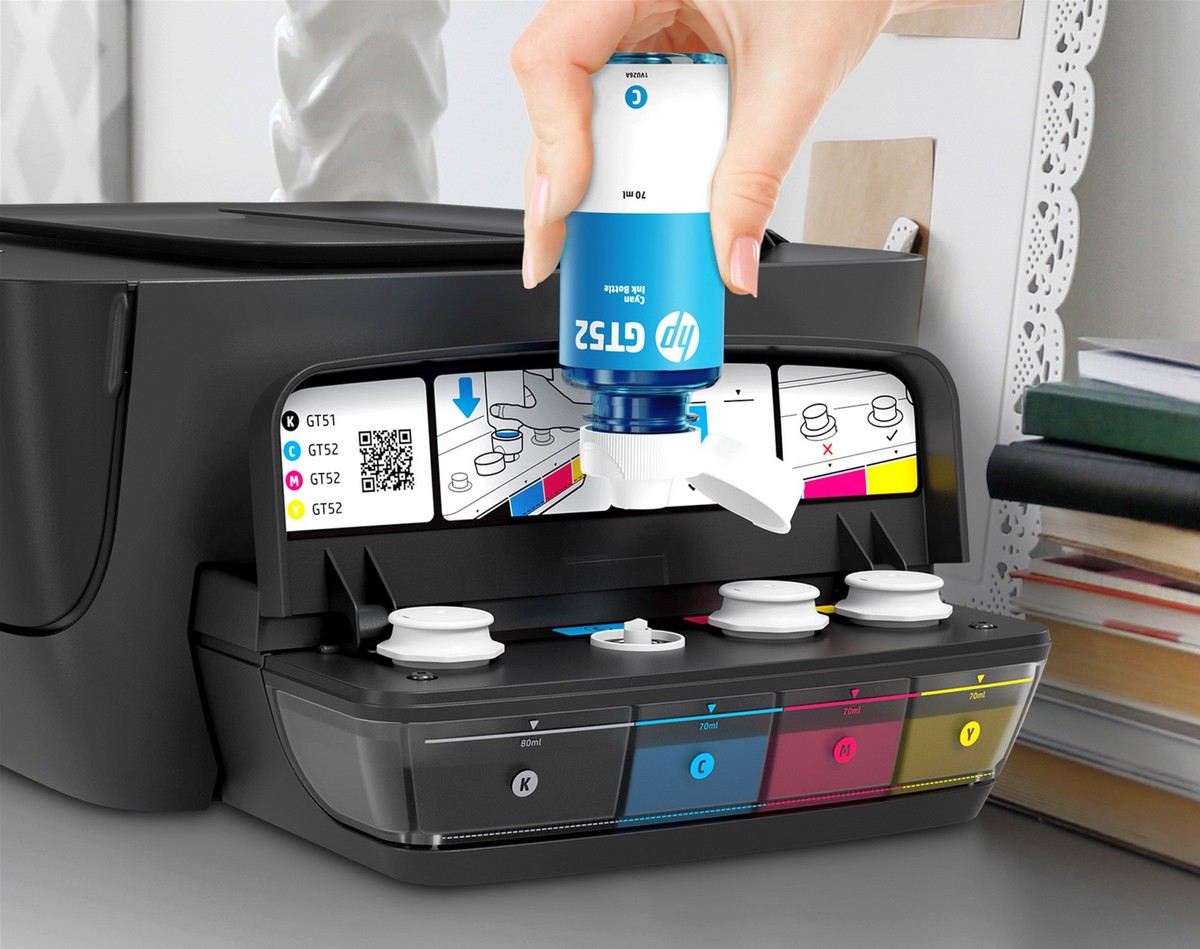 |
| Factory CISS provides a visual indication of the level of ink remaining in the tanks; they are easily and quickly refilled with paint. |
CISS does not affect print quality (it depends only on the ink used), does not damage the printer or MFP, and is often compatible with any type of consumables. Built-in continuous ink supply systems are expensive, so they are mainly used in expensive models. For simpler printers, compatible CISS are available, purchased and installed separately.
The debut of a continuous toner supply system on board laser printers took place in 2019. The first cartridge-free products were devices from the HP Neverstop Laser product line.
 |
| A special syringe with toner is inserted into the “filling neck” of HP Neverstop Laser cartridgeless laser printers. |
Instead of a traditional cartridge with ink powder , laser printers and MFPs of the family use an original toner supply device. The refill kit for them is made in the image and likeness of a large syringe of a closed design, from the spout of which not a single crumb of toner will spill. The technology is just getting on its feet, but its potential is truly enormous.
Printing photos
No digital photograph can compare with warm, lamp-based photographs on paper. You can print them yourself on a good inkjet printer or MFP. As we found out above, inkjet printers are best suited for printing photographs. The more ink cartridges a printing equipment uses, the juicier and richer the photos it produces will be. Also, when it comes to photo printing, the printer resolution is important - it should start at at least 4800x1200 dpi.
 |
| Inkjet printers and MFPs with high print resolution are best suited for printing photographic materials. |
Additional functions play an important role when choosing an inkjet photo printer. For example, support for cloud printing services, which allows you to print images remotely. The built-in card reader and USB port for direct printing of photo materials from external drives may be useful. Finally, Wi-Fi Direct and Apple AirPrint technologies allow you to connect other Wi-Fi devices directly to the printer - without using a router or local network.
Mini-printers for printing photos have now entered the era of strong growth. It is necessary to dwell on their ins and outs in more detail.
Portable printing devices
Compact printers mostly print on A6 and A8 paper. Copies for A4 sheets are found much less frequently among printing equipment with the “mini” prefix, which is due to their larger dimensions. Still , the main emphasis in portable printers is on the most convenient sizes for regularly carrying the device from place to place.
 |
| Mini photo printers usually fit easily into the palm of your hand and print small pictures directly from your smartphone using wireless connection protocols. |
Only a few models of inkjet printers and “pocket” photo printers, which rely on sublimation printing technology, are produced in a portable form factor. A small photo printer is convenient for quickly printing photos or business cards from a smartphone via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth wireless channels (including directly from social networks). How about “fast”? “Portables” take up to 1 minute to take one full-color photograph. pure time. Many models of such printing equipment are equipped with a built-in rechargeable battery for autonomous power supply.
Printing stickers and labels
When developing your business, you often need to print stickers and labels in your corporate style. Classic inkjet printers and high-resolution MFPs successfully cope with this task when using appropriate paper. They also often implement the ability to print on CDs, which is no longer so in demand in the modern era. Printing devices of this kind support direct printing from cameras, mobile phones via Bluetooth, cloud services, memory cards and external USB drives.
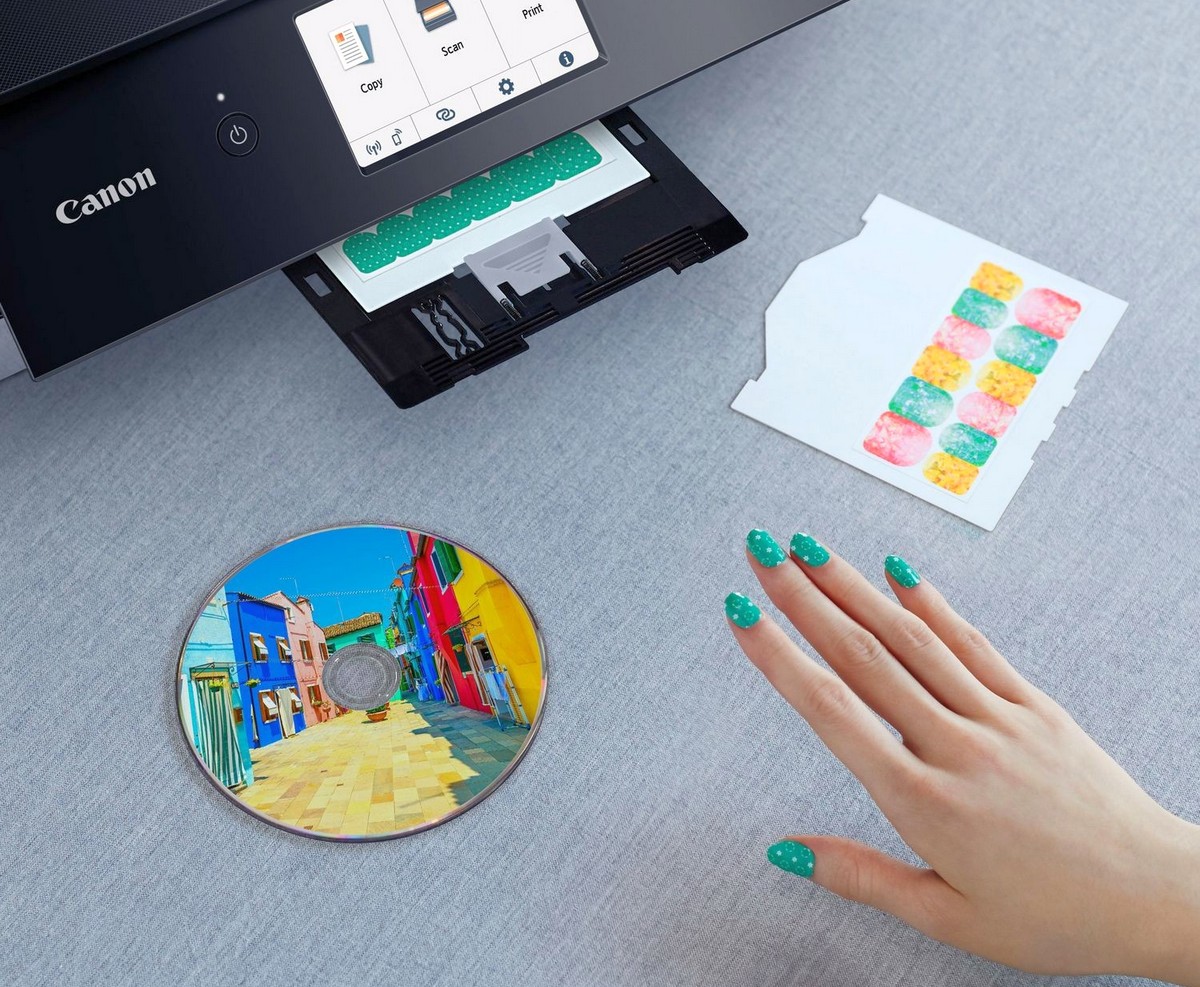 |
| Many inkjet printers and MFPs are great at printing stickers and labels, and some can print to CDs. |
But textile printers for printing on fabrics and heat presses for printing on cups are specialized professional equipment that has little in common with traditional home and office printers. This also includes ultraviolet printers that use UV-curable inks.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials
























































































