Automotive Lights: Frequently Asked Questions
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

1. What types of car lamps are there?
Car bulbs differ from each other in many ways. At a minimum, they are classified by type, and if we go into detail, also by base types. We have covered this in detail in a separate article , “Types, Bases, and Marking of Car Bulbs.” Here we will briefly mention the common types of car bulbs. So, they are:
- halogen ;
- xenon and bixenon ;
- light-emitting diodes (LED).
Structurally, halogen models are classic lamps with a filament and a gas-filled glass bulb(inside it is filled with halogen vapor, hence the name). Halogen bulbs are widely used for both low and high beams. They produce a natural yellow-white glow, are compatible with reflector and lensed optics. Halogens are inferior to other types of bulbs in durability and brightness, but they are cheaper.
Xenon lamps do not have filaments in their design, and their glow is provided by the passage of current between refractory electrodes in a xenon gas environment. Such bulbs emit bright pure white light, but they are suitable for installation only in lensed optics. An exception to the rule is lamps marked R at the end (for example, H7R), which are also suitable for reflector headlights. For xenon to work, specialized ignition units will need to be additionally introduced into the vehicle's electrical circuit. A separate type of xenon is bi-xenon lamps, capable of providing both low and high beam.
LED bulbs are used literally everywhere in a car: in headlights, side lights and brake lights, auxiliary lighting systems, etc. As the main light sources , LED bulbs boast the highest brightness parameters and the longest possible service life(often tens of thousands of hours of trouble-free operation). LED bulbs are often installed in standard sockets, but due to the presence of radiators and cooling fans, LED bulbs may differ slightly in size from classic halogen lighting equipment. As in the case of xenon, LED is recommended to be installed only in lensed optics.
2. Which car lamps shine brighter and which illuminate the road better?
Xenon and LED lamps produce the highest brightness of the luminous flux, but conventional halogen bulbs often shine the worst. Long Life halogen lamps, which are available from many reputable manufacturers, shine better and last longer. On average, the luminous efficiency of halogen lamps is about 25 lm per 1 W of consumed electricity, while for LED lamps this figure is approximately 4-5 times higher (up to 100 lm per 1 W). That is, LED bulbs consume much less energy to create brighter light.
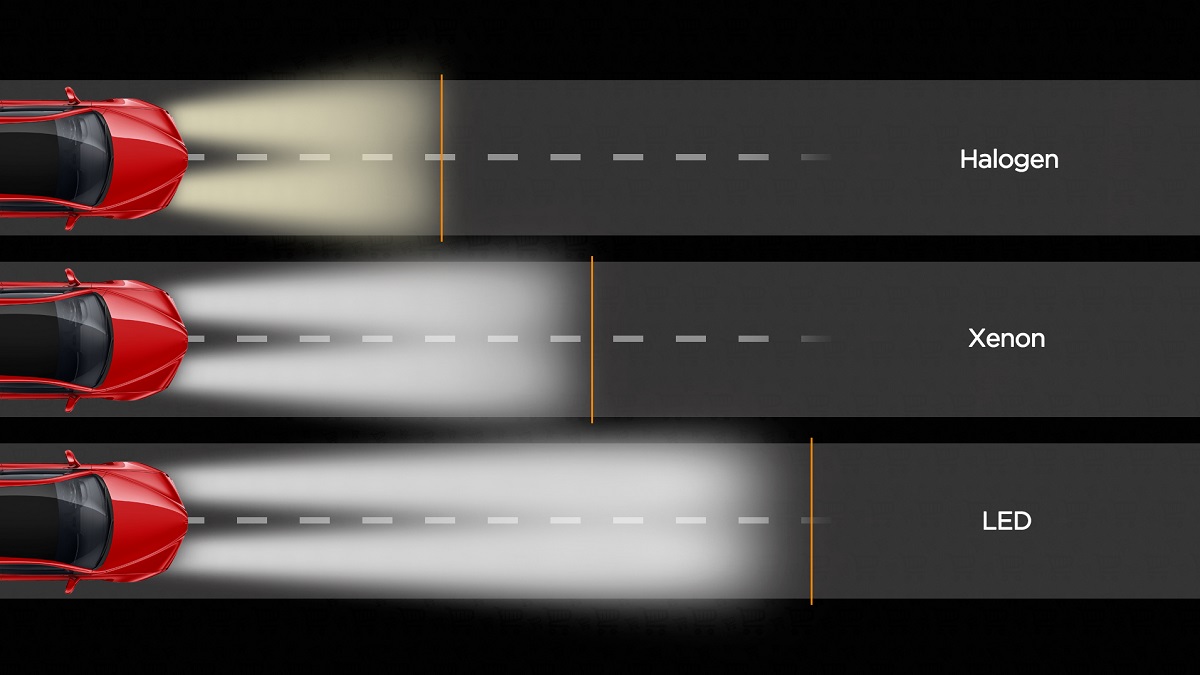
The road is best illuminated by properly selected lamps. For example, halogen bulbs are suitable for reflector headlights. After all, xenon and LED emit light in a wider range, and this leads to its incorrect distribution and promises to blind oncoming drivers. Xenon and LED bulbs are allowed to be installed in headlights with lenses. The greater their luminous flux in lumens, the better they will illuminate the road.
3. Is it possible to install higher power bulbs in the headlights?
The standard wiring in the car is designed for certain power parameters. Installing more powerful lamps in the headlights can result in the wiring melting and pose a fire hazard. In addition, the car's headlights are also designed for a certain thermal mode - powerful bulbs, although they shine brighter, also heat up more. This causes the reflectors to burn out, the glass in the headlights to become cloudy, and other similar problems to arise.
Installing more powerful bulbs is only allowed if the lighting system is upgraded: wiring, headlights and other components. However, such re-equipment is not always legal. From the point of view of the letter of the law, the use of powerful bulbs also raises questions - in many European countries they may be prohibited. Light sources in headlights must correspond to the type of light module specified by the manufacturer in the operating documentation for the car.
4. What kind of light bulbs should not be installed on a car?
There is no single generally accepted regulation that prohibits the use of certain lighting equipment on board a car. Each country has its own rules and regulations on this matter. It is definitely forbidden to install xenon and LED bulbs in reflector headlights(with the exception of some models with the R marking at the end). Such lamps can potentially be installed in lensed optics. It is allowed to use bulbs with white, yellow and orange lights in the front lighting devices of a car. Any other shades are not allowed.
5. Which light is better for a car: white or yellow?
The emission spectrum of headlight bulbs is determined by the color temperature in Kelvin. The higher its value, the "colder" the lamp will have. And vice versa.
According to color temperature, car bulbs can be divided into the following subcategories:
- yellow-white light(up to approximately 3700 K);
- bright white light(from 3700 K to 4500 K);
- white-blue light(from 4500 K to 5500 K);
- blue light(over 5500 K).
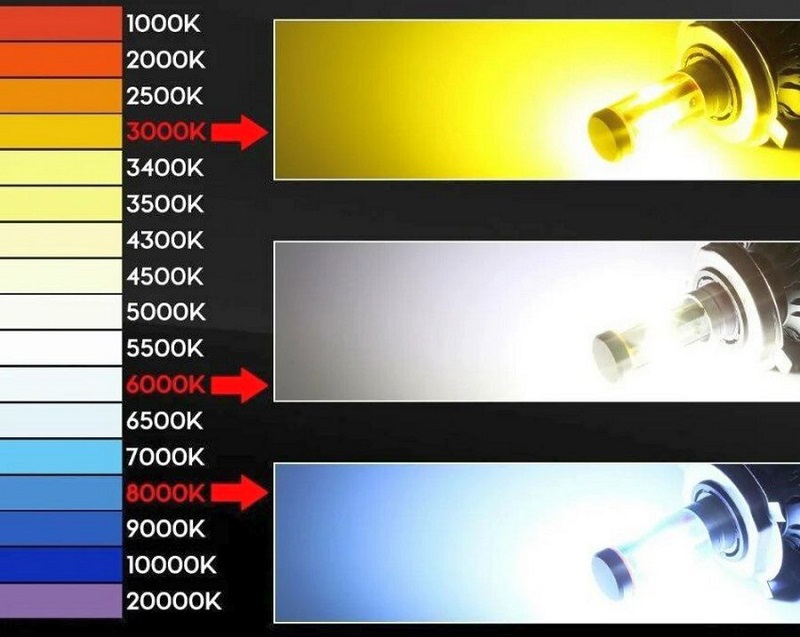
The maximum similarity to natural daylight is provided by bulbs that produce a color temperature of about 5000 K. They will be highly effective in the dark. Yellow shades of light are better suited for adverse weather conditions, which is why "warm" bulbs are often found in fog lights. But bulbs with a temperature over 6000 K give a weak light effect, but the light from them looks attractive. In many countries, such car lamps are banned.
6. What light shines better in the rain?
As we have already found out in the previous point, from the point of view of comfort for the human eye, the best are bulbs of about 5000 K. But such a color temperature reduces the illumination of the road in rainy and foggy weather, as well as in heavy snowfalls - the fact is that white light is reflected from the falling precipitation. In adverse weather conditions, lamps with a color temperature of up to 3700 K show themselves best. The rays of light from them are not scattered and are not reflected from drops of moisture.
7. What is H7 on bulbs?
In the segment of lighting equipment for cars, there are two key industry standards, according to which the marking of bulbs is carried out, or more precisely, their sizes and bases. This is described in detail in the article "Types, bases and marking of car lamps".
The most common designations of lamps in everyday life are those according to the standards of the European Economic Council (ECE). Halogen, xenon, and LED bulbs in headlights are usually marked with the Latin letter H and a number after it (or HB for models with an American-style base). Standard (factory) xenon bulbs are designated with the letter D, and small auxiliary base lamps are designated with the symbols P, T, and W.

The principles of marking car bulbs according to IEC and DIN standards are slightly different. All of them are described in the above-mentioned article. In practice, the designations of standard sizes and bases will serve as a guide for finding a lamp for specific needs. So, if the headlight had a bulb marked H7, then a model with a similar base must be selected to replace it.
8. How are halogen lamps different from regular light bulbs?
Halogen lamps are essentially a modification of traditional incandescent bulbs with a tungsten spiral. However, to reduce tungsten evaporation and prevent black sediment from falling inside the bulb, "halogens" are filled with halogen vapors (usually bromine or iodine). Inert gas under pressure slows down the process of burning out the spiral, thereby increasing the light output of the lamp and extending its service life.
Halogen bulbs are commonly used in headlights, while conventional incandescent bulbs are widely used in auxiliary lighting systems: side lights, brake lights and turn signals, license plate lights, interior lighting, etc.
9. Is it possible to install LED lamps instead of halogen ones?
LED bulbs are available in the same base options as halogen bulbs. Therefore, in theory, LED bulbs will easily fit into the headlight, although there are exceptions to this rule - due to the presence of a radiator or cooling fan in the LED design, LED bulbs may have slightly different sizes and shapes. It is important to make sure that the new bulb will fit into the headlight.
The configuration of the vast majority of halogen reflector headlights is not designed to diffuse light from LED lamps. This is why the lighting system's operation mode is disrupted. LED bulbs should only be installed in lensed optics, then all questions regarding the legality of using such lighting are removed.

It may be necessary to introduce special “cheats” into the vehicle’s electrical circuit via the CAN bus.
In some cases, an additional "cheat" in the LED lamp design may be needed - LEDs consume less power and the car's on-board electronics may simply not see them, which is why the on-board computer considers the reduced power as a headlight malfunction. A "cheat" based on the CAN bus helps to avoid such problems.
10. How to distinguish between a low beam and high beam bulb?
There is no specific breakdown into low and high beam bulbs - the applicability of a car bulb depends more on the design features of the headlight than on the characteristics of the light source. Often, low and high beam bulbs are located in different sections of the headlight: a separate bulb turns on the low beam, which is directed down onto the road, another separate one is responsible for the high beam - it is intended to illuminate the road at a long distance.
Let's look at the example of halogen lamps. One of the most common options is a combination of H7 bulbs for low beam and H1 for high beam. But bulbs with an H4 base are combined and contain two spirals. One filament is responsible for the low beam, the second for the high beam.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials





















































































