Types, bases and markings of car lamps
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

Lighting is used literally everywhere in a car. And of course, the bulbs for headlights and interior lighting will be strikingly different from each other. Before we go into detail, let's first look at the common types of car bulbs.
1. Types of car lamps
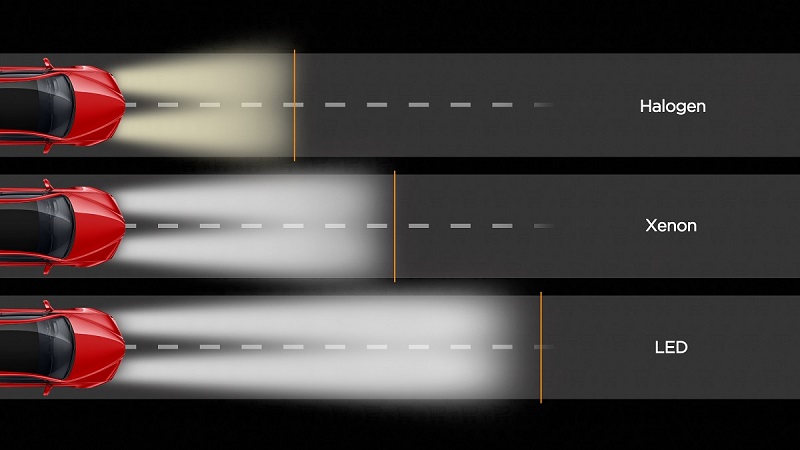
Globally, car bulbs are divided into three large camps: halogen, xenon (and also bi-xenon), and light-emitting diode (LED).
1.1 Halogen car lamps
In essence, these are classic incandescent lamps with a tungsten filament and a fiberglass body. Headlamp lamps are filled with halogen vapors, which enhance the luminous flux and extend the glow resource. But auxiliary models are classic incandescent lamps without gas filling.
Halogen low and high beam lamps usually give a natural yellow-white shade, they can be used with both reflector and lensed optics. In general, this type of lamp is the most popular as a head light.
Advantages of halogen bulbs:
- universality of application - halogen bulbs have standardized dimensions and filament position, and they are also suitable for reflector and lensed optics;
- affordable cost - in terms of other types of light bulbs, halogen bulbs are the cheapest.
Disadvantages of halogen bulbs:
- low resource - on average from 500 to 1000 hours;
- low power-to-brightness ratio - for 1 W of power, a halogen car lamp produces on average about 25 lm of brightness;
- heating - this leads to gradual burnout of the reflector and a decrease in the intensity of the light flux.
1.2 Xenon and bi-xenon car lamps
Xenon lamps are used exclusively in headlights (although some folk craftsmen manage to install xenon in fog lights and even in reversing lights). Such bulbs do not have filaments, so they are not afraid of shaking and vibrations when moving on a bad road surface. Their sealed flask is filled with xenon gas, and the operating principle is based on an electric discharge between refractory electrodes in a gas environment.
Xenon car bulbs emit pure white light of very high brightness - in this regard, only some LED lamps can compete with them. But for the correct installation of xenon lamps, it is necessary to equip the headlights with lenses. Xenon in reflector headlights potentially blinds oncoming traffic - this is at least disrespect for other road users and at most - fines for violating the lighting mode.
Classic xenon bulbs have one brightness mode. They are most often installed on low beam, and for high beam, conventional halogen lamps are used. There are also bi-xenon car bulbs that can provide both low and high beam. Note that for xenon to work, you will need to additionally introduce ignition units into the car's electrical circuit - they are initially supplied in xenon kits.
Advantages of xenon bulbs:
- high brightness;
- long service life and excellent reliability.
Disadvantages of xenon bulbs:
- Suitable for headlights only;
- installation is possible only in lensed optics;
- the need to use ignition units;
- potential legal problems.
1.3 LED car lamps
LED lamps are rapidly gaining popularity in all spheres of life. They have not bypassed the automotive segment either - LED bulbs are widely used in headlights and auxiliary lighting systems. Their competitive advantages over other types of bulbs include extremely low energy consumption with high light output, versatility of use, and a long service life.
In headlights, LED bulbs are often installed on standard halogen connectors. However, 100% compatibility is still not guaranteed - the design of LED lamps usually includes radiators and cooling fans, which increases their dimensions compared to traditional halogens. It is advisable to install LED bulbs in lensed optics, since LED in reflector headlights can blind oncoming drivers, and its legality of use will be highly questionable by the traffic police. In many European countries, non-standard lighting systems are punishable by large fines.
Advantages of LED bulbs:
- high brightness;
- long service life (over 30 thousand hours) and excellent reliability;
- universality of application - LED bulbs are suitable for almost any headlights and are available in versions for all auxiliary lighting systems.
Disadvantages of LED bulbs:
- price - high-quality LED bulbs are more expensive than halogen and xenon bulbs;
- enlarged housing (due to the need to dissipate heat) - LED bulbs are not suitable for all headlights where compact halogen bulbs are installed;
- dependence on power supply stability for high-quality and stable glow.
2. Principles of marking
The need to use generally accepted principles for designating car bulbs is obvious. Today, two systems for their marking have become widespread: according to the standards of the European Economic Council (ECE), as well as the IEC and DIN specifications (International Electrotechnical Commission and German Institute for Standardization).
The ECE standard divides car bulbs by size. It is not entirely correct to call them sockets, but the sockets of lamps of different sizes will also differ. For each size, specifications of technical indicators are additionally approved, due to which a too powerful lamp a priori cannot be installed in an inappropriate place. Thus, for the popular 12-volt H7 bulb, the power is declared at about 55 W and the luminous flux is about 1500 lm.
| ECE marking | Features of the light bulb |
|---|---|
| H, HB | Initially, these are halogen lamps (Halogen). However, the same markings are used for xenon and LED bulbs, the shape and base of which completely correspond to the halogen "original". The HB designation is used for halogen lamps with a peculiar shape of the base in the American style. |
| D | Standard (factory) xenon bulbs. |
| T | Miniature base lamps. |
| R | Lamps with a 15 mm base and a bulb up to 19 mm in diameter. If the letter R is indicated in the middle of the marking, this designates red lamps (e.g. PR21W). |
| P | Lamps with a 15 mm base and a bulb up to 26.5 mm in diameter. |
| W | If the letter W is indicated at the beginning of the marking, it means that the bulb is equipped with a glass base. If the designation W is at the end of the marking, it is the power of the bulb in watts (W). |
| Y | Light bulbs with yellow or orange bulbs. |
| C | Spotlight lamps, in which the bulb is located between two bases. |
The conventional T4W bulb stands for miniature base lamp with a power of 4 W. And the PY21W model is a yellow lamp with a 15 mm base and a diameter of up to 26.5 mm, yellow, with a power of 21 W.
In the marking of car bulbs according to IEC and DIN standards, three separate categories of designations can be distinguished. The table below covers common marking options:
| IEC and DIN marking | Features of the light bulb |
|---|---|
| P | Flanged lamps. |
| B.A. | Pin bulbs with symmetrical arrangement of contacts (pins). |
| BAX | Pin lamps with one of the pins offset along the radius (X axis on the coordinate plane). |
| BAY | Pin bulbs with one of the pins offset in height (Y axis on the coordinate plane). |
| BAZ | Pin bulbs with one of the pins offset both in height and in radius (Z axis on the coordinate plane). |
| E | Lamps with screw base. |
| W | Light bulbs with glass base. |
| SV | Spotlight lamps, in which the bulb is located between two bases. |
| Flask designation | Flask shape |
| B | Oval. |
| G | Round. |
| T | Oblong. |
| S | In the shape of an “eggplant”. |
| RP | Narrow at the bottom and wide at the top. |
| Contact designation | Number of contacts |
| s | One. |
| d | Two. |
| t | Three. |
| q | Four. |
| p | Five. |
For example, let's take a bulb marked P43d - this is a flange bulb with a diameter of 43 mm, two-pin. And the conventional model BA15s is a single-pin bulb with a diameter of 15 mm.
3. Headlamp sockets
The same sizes of car bulbs are usually used in headlights and fog lights. For better clarity , the most popular socket options are presented in a table:
| Size (base) ECE | IEC and DIN socket |
|---|---|
| H1 | P14.5s |
| H3 | PK22s |
| H4 | P43t |
| H7 | PX26d |
| H8 | PGJ19-1 |
| H10 | PY20d |
| H11 | PGJ19-2 |
| H27W/1 | PG13 |
| HB3 | P20d |
| HB4 | P22d |
| D1R | PK32d-3 |
| D1S | PK32d-2 |
| D2R | P32d-3 |
| D2S | P32d-2 |
| D4R | P32d-6 |
| D4S | P32d-5 |
The table covers the most common types of bases. In general, the applicability of different types of car bulbs is shown in the example image:
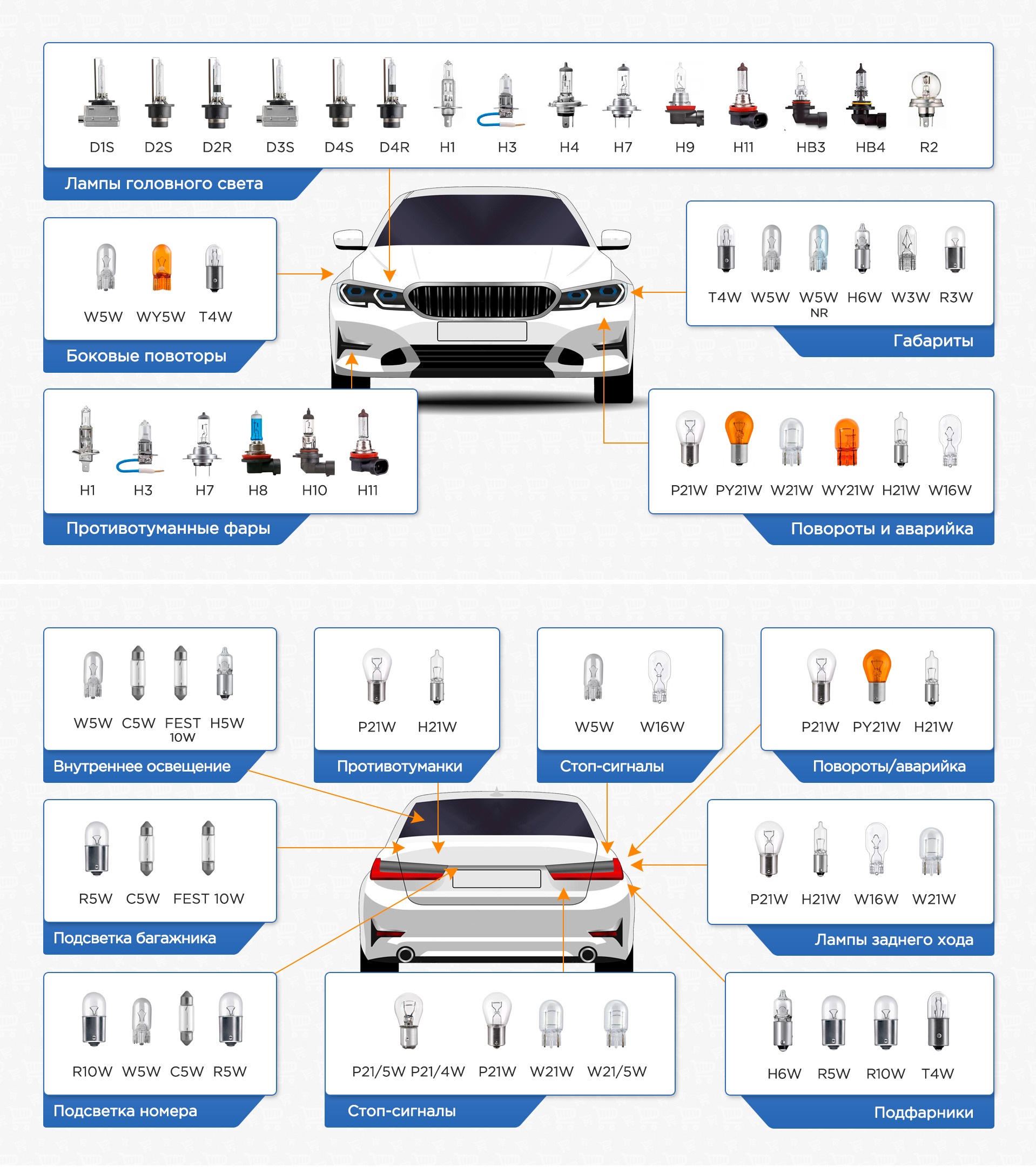
4. Bases in auxiliary automotive lamps
Auxiliary bulbs are any lighting equipment that is not installed in the headlights. These can be bulbs for turn signals, brake lights, side lights, rear license plate lights, trunk lights, interior lighting, etc.
The most common formats of sockets in auxiliary car bulbs are presented in table form:
| Size (base) ECE | IEC and DIN socket |
|---|---|
| C5W | SV8.5 |
| C10W | SV8.5 |
| H6W | BAX9s |
| P21/5W | BAY15d |
| P27W | W2.5x16d |
| PSX26W | PG18.5d-3 |
| PY21W | BAU15s |
| R5W | BA15s |
| T4W | BA9s |
| W5W | W2.1x9.5d |
| W21W | W3x16d |
| WY5W | W2.1x9.5d |
When choosing car bulbs, it is convenient to follow a simple principle - whichever bulb burned out, you need to select the same one to replace it. If access to the bulb is difficult, which often happens in headlights or rear lights of a car, you should use the car's instructions. Some websites have implemented the ability to select bulbs by brand and year of manufacture of the vehicle or even by VIN code.
But what definitely cannot be replaced by yourself is burnt-out LED headlights and LED taillights. Factory LED optics are changed or repaired at service stations and authorized car service centers. And if it cannot be repaired, then the entire headlight will have to be replaced - this is extremely expensive.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials

























































































