HDMI 2.2: Detailed Analysis
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

1. Learn more about HDMI 2.2

First, a little nerdiness. So, HDMI is a high-definition digital multimedia interface capable of transmitting high-quality audio and video signals simultaneously. It was developed in 2002 and became a replacement for VGA, DVI, S/PDIF and other less fortunate or outdated interfaces. In fact, it is one of the most used interfaces today, operating in more than 14 billion devices, including TVs, monitors, laptops, receivers, gaming consoles and many other devices.
The previous version, HDMI 2.1, was introduced back in 2017. It brought support for ALLM and VRR, the ability to play content in 4K + 120Hz and 8K + 60Hz modes, and many other innovations that were ahead of their time and provided room for maneuver for several years to come.
Here are some of the features of HDMI 2.2:
- Enhanced Bandwidth: HDMI 2.2 has a maximum bandwidth of 96 Gbps, which is 2 times the bandwidth of HDMI 2.1 (48 Gbps).
- Higher resolution: Although most modern technology and content is designed for 4K, the new format can play 10K video at 120 Hz or 8K at 240 Hz. In theory, it can even work with 12K and 16K resolutions, but with certain limitations. For comparison, HDMI 2.1 had a peak mode of “4K + 120 Hz”, and 8K content is only played in DSC compression mode with color coding limitations.
- Synchronization of signal between several connected devices: the new Latency Indication Protocol (LIP) is designed to minimize delays between sound and picture when outputting a signal to different devices. For example, if sound is output through an AV receiver or soundbar, and video is output to a TV or monitor, the signal processing time may vary, causing the sound to lag slightly behind or ahead of the picture. LIP solves this problem by adding time stamps to the audio signal to automatically adjust the delay time.
- Gaming Optimization: Although HDMI 2.1 supports 4K + 120Hz, not all HDMI 2.1 devices implement this mode, as manufacturers may limit functionality due to implementation features and the use of cables that are not capable of providing the declared bandwidth. The new HDMI 2.2 version with support for 10K + 120Hz should completely solve this problem. Also, according to rumors, ALLM Plus and QFT 2.0 support may appear in subsequent versions to optimize signal transmission latency in games.
2. HDMI 2.2 video and audio support
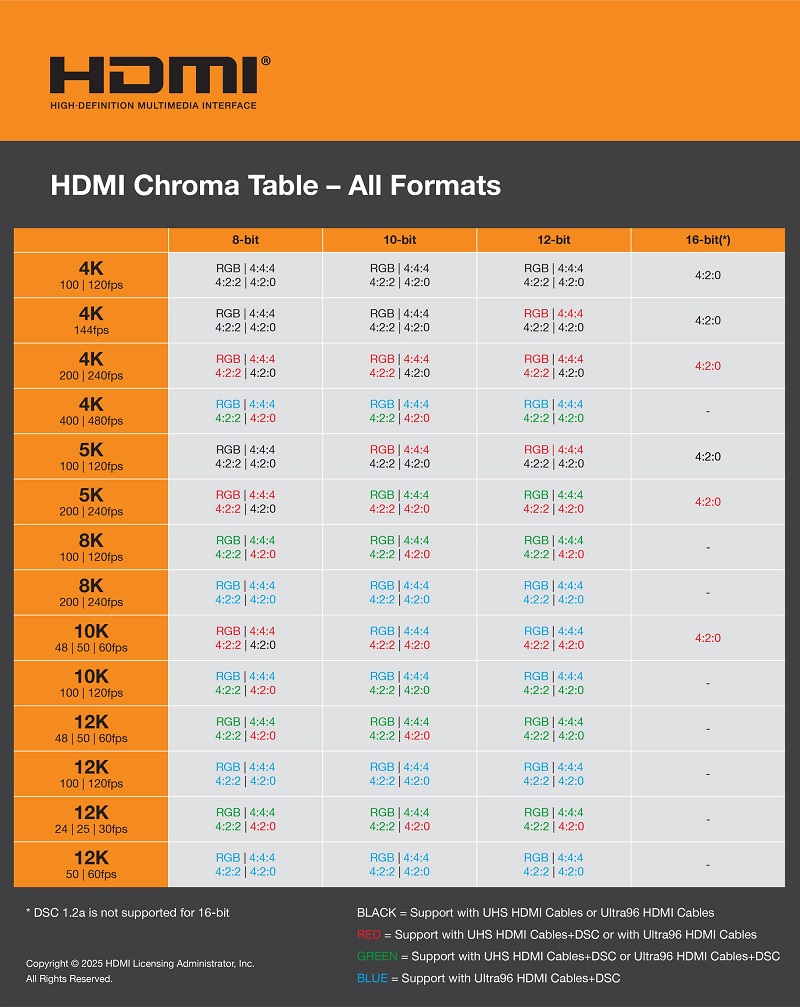
According to the HDMI Licensing Administration, HDMI 2.2 can transmit uncompressed 4K video at 240 frames per second or 8K at 60 frames per second, while supporting full 10- and 12-bits color. Higher resolutions require compression to keep within the 96 Gbps bandwidth. In comparison, DisplayPort 2.1b offers a maximum bandwidth of 80 Gbps.
HDMI 2.2 also uses an updated version of FRL (Fixed Rate Link) — a replacement for the outdated TMDS. FRL technology supports up to four data transmission channels, dynamically adapts the speed depending on the connection, and uses more efficient step coding. The first version of FRL debuted in HDMI 2.1 in 2017 — at the time when Microsoft released the Xbox One S with 4K support, and Apple began distributing 4K content in iTunes. It was the introduction of FRL that largely ensured support for VRR technology and the ability to play HDR formats. The updated version of FRL is focused on the future: it supports higher resolutions and refresh rates up to 460 Hz, ensuring compatibility even with top-end TVs and premium monitors.
While the press release doesn't give much detail on the new audio capabilities, it's safe to assume that HDMI 2.2 retains all the features of HDMI 2.1. These include support for 32 audio channels, sampling rates up to 192 kHz, and eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel). The latter simplifies the delivery of multi-channel audio, including Dolby Atmos and DTS:X, ensuring high-quality, lossless audio when used with compatible devices.
3. HDMI 2.2 Compatibility: What You Need to Know?

To fully utilize all the capabilities of HDMI 2.2, a full chain of compatible devices is required. That is, both the signal source (for example, a gaming console, media player or video card), and the output device (TV or monitor), and the cable must support the new standard.
At the moment, even the most modern TVs, gaming consoles, and video cards are not capable of working with HDMI 2.2. Unfortunately, it is not possible to update existing devices to HDMI 2.2. The HDMI Licensing Administration plans to release official specifications for manufacturers in the first half of 2025, after which the development and testing of new equipment will begin. As experience from previous generations shows, this process can take from two to four years.
In addition, HDMI 2.2 will require a new cable with increased bandwidth. Older HDMI cables may not be able to handle the new standard. To prevent counterfeiting, the HDMI Forum has introduced Ultra96 HDMI certified cables, which will be marked with special anti-counterfeiting marks. The Ultra96 badge on the packaging will allow customers to easily identify genuine products.
4. Who is HDMI 2.2 designed for?

While HDMI 2.2 offers impressive capabilities, its potential is not for everyone. For movie fans, its benefits seem redundant, as most movies and TV shows are released in 4K at 24 frames per second. Sports broadcasts are often broadcast at 60 frames per second, and the higher frame rates do not provide any noticeable benefits.
Where HDMI 2.2 really gets interesting is for gamers and high refresh rate enthusiasts. At CES 2025, several manufacturers unveiled monitors and TVs that support 4K at 480Hz and even 8K at 240Hz. While even the most powerful gaming PCs struggle to reach those numbers today, HDMI 2.2 ensures that the standard will match DisplayPort and USB C in terms of bandwidth and technological flexibility.
However, there are questions here, because at the same time at CES 2025 a new version of DisplayPort 2.1b with similar technical parameters was presented. DisplayPort 2.1b is also more focused on gamers, but, unlike HDMI 2.2, it is already at the stage of active implementation. For example, the new NVIDIA GeForce RTX 50 video cards on the Blackwell architecture are equipped with DisplayPort 2.1b connectors with the ability to connect displays with a resolution of up to 8K and a refresh rate of up to 165 Hz.
5. Conclusion
Overall, HDMI 2.2 is future-oriented — it paves the way for new gaming technologies, premium TVs and monitors with 8K matrices, as well as augmented and virtual reality systems, where high frame rates play a key role. And if after the announcement of version 2.2 you decide to slightly postpone the purchase of a new TV, then don’t — the implementation of the new standard will take several years, and it will initially be used in premium technology. And there is no point in rushing, in principle — the technical capabilities of the current version of HDMI 2.1b cover the needs of most users.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials




