The principle of operation of the refrigerator
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

Moreover, the "heart" is not necessarily one — they are also produced with two, for two-chamber refrigerators. The presence of an additional motor in this case can make it possible to turn off the cameras individually, which gives advantages in ease of operation.
 |
The unique property of a refrigerant is its ability to change from a gaseous state to a liquid state and vice versa. Inside the refrigerator, this happens in the condenser and evaporator. At the same time, the energy spent on the transition between aggregate states cools the air in the refrigerator, which is necessary for the preservation of products.
Refrigerator device
The refrigerator body may contain one, two or more food storage chambers. Refrigerator doors with a rubber seal isolate its interior. The piston of the motor-compressor pumps freon refrigerant, warming it up. Control elements are responsible for the frequency of operation of the compressor. The tubes through which the refrigerant circulates are hidden inside the walls of the case.
Mandatory for conventional refrigerators, the presence of a weeping evaporator — a chilled metal plate mounted on the back panel — has become unnecessary in the No Frost system. It is often found in modern refrigerators, and its popularity is well deserved — because with it you can forget about the freezing of ice on the walls, all these terrifying layers in old refrigerators. The “trick” is that the fan “drives” the cooled air through the refrigerator, while the evaporator responsible for cooling is more like a radiator and is located only near the freezer compartment.
How does a refrigerator work
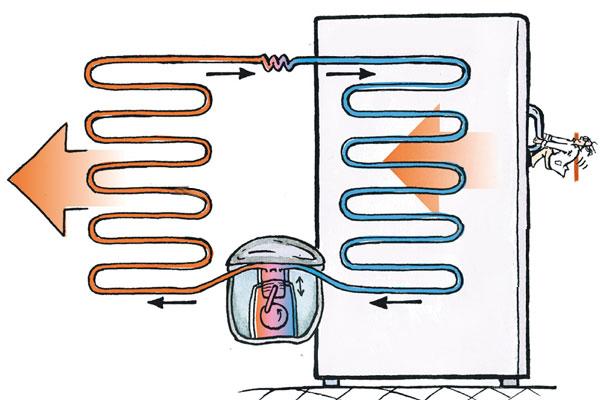
The operation of the refrigerator is based on three "pillars" — isolation (refrigerant in the pipes, air inside the refrigerator), movement (heat and refrigerant) and creation of a difference (pressure and temperature).
If isolation from the external environment is on the conscience of materials — from rubber door seals to aluminium tubes, then the pressure difference is provided by a capillary tube.
Two elements are located "on opposite sides of the barricades" from this tube in terms of pressure — an evaporator and a condenser.
Evaporator — low pressure, the refrigerant enters there in a liquid state of aggregation, as a result of which it boils. As a result of the absorption of heat, we obtain the cold necessary for storing food.
Condenser — high pressure, here the refrigerant gives off heat, returning to a liquid state. Heat is released to the outside. The tube at the back of the refrigerator, warm to the touch, is the condenser.
Well, the movement of the refrigerant through the system of "vessels" is ensured by the active operation of the compressor. Along the way, the compressor raises the temperature of the refrigerant, which at the same time changes its state of aggregation, boiling.
Thus, the main working element is a refrigerant that changes its state of aggregation. The responsibility for this transition lies with the operation of the engine — the compressor that drives it through the tubes, and the capillary that creates the pressure difference. The coolness, so necessary for us for domestic needs, we owe to the evaporator — a “piece” of metal invisible to our eyes. Well, the condenser allows the refrigerant to continue the cycle.
Refrigerator diagram
A key element of the repairmen's worries — the compressor — is usually located at the bottom of the refrigerator. In the presence of a second compressor, the circuit becomes a little more complicated, but basically remains the same, including a coil of tubes and plates. Additional elements, such as a filter-drier that protects the capillary tube from clogging, an after-boiler — a container between the evaporator and the compressor, which is necessary so that no refrigerant enters the compressor, a fan for cooling the motor, lighting and various control systems can vary without changing the basic device. There are also protective elements — a fan to cool the "heart" of the refrigerator from overheating, various relays, a thermostat.
Each specific model has its own characteristics, the task of manufacturers is to improve the concept in detail, achieving energy efficiency and ergonomics.
Refrigerator compressor operation
The most common version of the compressor — piston — differs depending on the specific modification. In its most general form, the crankshaft rotates inside a sealed casing. The movement of the piston forces the refrigerant into the condenser in a reciprocating manner. The valve system regulates the ingress of gas.
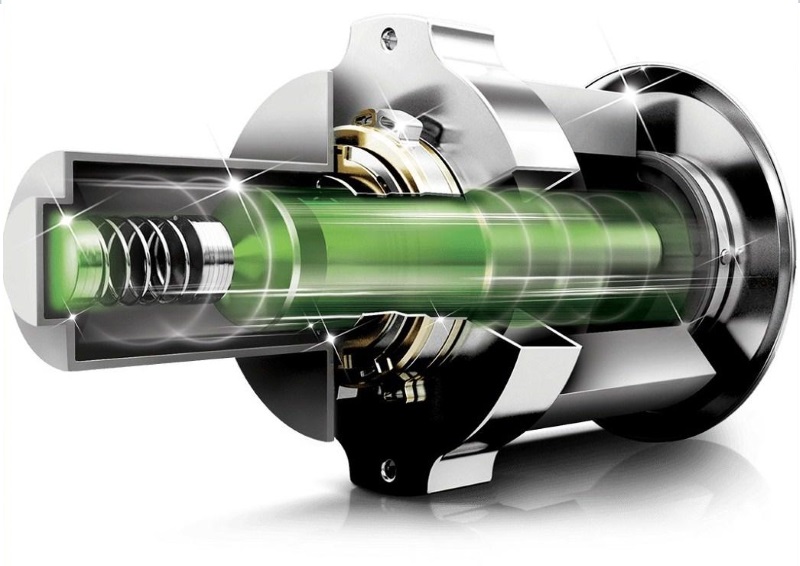 |
However, in household refrigerators, the structure of the piston itself can also be with a different mechanism. In the presence of two compressors in the refrigerator, a crank-rocker is used, for a large volume and significant loads — a crank-rod. Replacing the crankshaft in the motor with AC power to the coil improves economy by making mechanics unnecessary.
Compressor operation diagram
The electric current, passing through the closed contacts of the thermostat, the thermal protection relay and the starting, as well as the working winding of the compressor, starts the operation of the latter.
 |
The start relay connects the starting winding of the motor to the circuit. Contacts are closed, the motor starts rotation. The bimetal plate of the thermal protection relay changes shape during dangerous heating, which can occur with a strong increase in electric current. In this case, the contacts open, turning off the engine. Also, the engine stops due to the opening of the thermostat contacts — the compressor turns off when the temperature reaches the set value.
The device of a single-chamber refrigerator
The evaporator is located in the upper part of the refrigerator, under it for a smooth decrease in temperature there is a tray, the closing / opening of the openings of which regulates the supply of cooled air to the chamber. The thermostat starts the compressor on/off cycle. Inside the pipeline of modern refrigerators there is a capillary tube that protects against condensate.
The device of a two-chamber refrigerator
In a two- chamber refrigerator, the thermal insulation of the partition separates the evaporators, separate for each chamber. The refrigerant is first pumped through the capillary tube to the evaporator in the freezer, and only after its temperature drops below zero on the Celsius scale, it enters the evaporator of the second — refrigeration — chamber. After freezing of the second evaporator, the thermostat stops the compressor.
When the evaporator heats up to a certain level, the compressor automatically turns on.
Freezer diagram
As part of a household refrigerator, the freezer should traditionally be at the top, as the cooled air sinks down due to the laws of physics. But in modern refrigerators, it can be both on the side and below. There is nothing magical here — it became possible thanks to exclusively technological innovations. In particular, the presence of two compressors or two circuits. Such engineering solutions increase the cost of products, but at the same time, the level of domestic comfort increases, which explains their growing popularity.
 |
Fundamentally, the device of a separate freezer does not differ from that of a refrigerator included in the composition. The fan system in dry freezing is the main difference from the drip defrost type.
During the heating season, hot batteries become real "eaters" of moisture.
One monitor is good, but two is better.
Maximum image quality in the smallest form factor.
We broadcast the image from the laptop to the TV via cable and "over the air".
A compact alternative to thermopot with the ability to heat water to the desired temperature.

















