How to choose a processor for a computer?
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

In the desktop processor market, the “war” between AMD and Intel has been going on for many years. There is a strong opinion that AMD products can provide more interesting solutions in the lower price range, while Intel has no competitors in the upper price range. Obviously, the most interesting thing is the middle price range, where there is a struggle for the user between the two giants with varying success.
The choice between these manufacturers will have to be made immediately and, most likely, for a long time, since the choice of motherboard depends on this. Each processor is designed to be installed in its own unique socket (aka Socket), each motherboard has only one such socket.
Which connector/socket to choose for AMD or Intel processors?
A large number of different connectors and their monotonous names may be discouraging at first, but in fact everything is as simple as possible. There are only a few types that are relevant for the mass user for both Intel products and AMD processors.
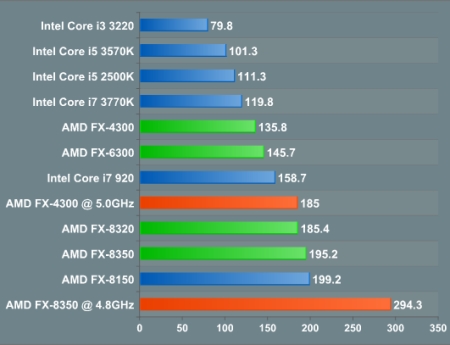 |
|
The power consumption of top AMD processors in the load reaches up to sky-high three hundred watts and above |
Intel LGA 1150 is one of the most popular solutions. You can install quite powerful (up to top-end) processors, ranging from Core i3 to some Core i7, for example, these models. Perfect for building a gaming or multimedia computer.
Intel LGA 1155 is an older version, which, however, has almost the same set of characteristics. Platform support has already ended and, for example, a new generation of Intel Core Haswell processors for this construct is no longer available. In other words: when it comes time to replace the processor, you will not be able to buy a new model within the platform - you will have to change the entire platform.
If you need maximum performance, then you should pay attention to the LGA 2011 connector - heavy artillery in the Intel family. Supports the installation of northern Intel Xeon processors, as well as ultra- productive Intel Core i7 3970X Extreme Edition. Perfect for those who are engaged in really resource-intensive tasks that require huge computing power.
The most popular solutions in AMD's camp are Socket AMD FM2 processors. Within the framework of the platform, 2- and 4-core processors are presented with good integrated graphics or without it, with support for their own Turbo safe overclocking mode. Solutions of this type can serve as a good option for both work and gaming systems.
AMD laboratories have also prepared their “secret weapon”, which, although it loses to Intel in top solutions, can provide the computer with the highest computing power and excellent multitasking. This applies to processors under Socket AM3+. The most powerful and productive solutions are created for this platform, but all of them are initially devoid of integrated graphics.
Concluding the story about the most popular platforms, let's pay attention to a number of motherboards with already built-in central processors. Such solutions are convenient in the sense that they allow you not to think about choosing the right platform, processor or video card and their compatibility with each other, and also save the user from unnecessary assembly problems. But the power of such systems is more likely to be enough to perform office tasks and simple, undemanding games. They can be a great solution for office computers or in situations of tight low-cost.
How to understand the hierarchy of the series of modern processors?
At one time, Intel made an excellent marketing move by launching a new family of Intel Core processors and distributing them into three separate lines, depending on performance.
Intel Core i3 - the younger brother in the family, direct competitors to the previous generation Core 2 Duo. Presented by 2-core processors with integrated graphics, designed for installation in entry-level computers. In its own rating of processors, Intel has three stars, while the older Intel Celeron and Pentium designs have one and two stars, respectively.
Intel Core i5 is the middle brother, designed for mid-range computers. Presented with 2 and 4-core models with increased clock speed and overclocking capability. The Turbo Boost automatic frequency increase mode has been implemented, some models have integrated graphics. Four star rating.
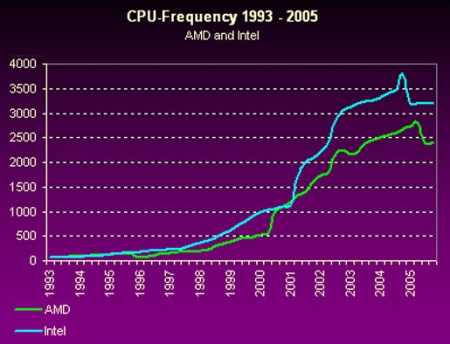 |
|
As can be seen from the graph, the trend of increasing clock speed has stopped a few more years ago, succumbing to multi-core and increased cache |
Intel Core i7 - the most expensive and productive solutions, represented by 4- and 6-core models for high-end desktop computers. The increased clock frequency, increased cache and support for a number of modern solutions practically deprive them of any serious competitors. Five stars in the Intel rating.
During its development, the Intel Core family of central processors has gone through several generations: Sandy Bridge(2nd generation, January 2011), Ivy Bridge(3rd, April 2012) and Haswell(4th, June 2013). Each brought many innovations, changed the process technology and energy consumption. But despite this, in terms of speed, the differences between processors of the same line, but of different generations, are very insignificant. And if you have an Intel Core i5 3570k processor installed on Ivy Bridge, then replacing it with a Core i5 4670k on Haswell, you may not even notice a difference in task execution speed.
As for the AMD camp, instead of convenient numbers, full-fledged “names” are used, but the logic is the same.
AMD Athlon II is a junior, low-cost solution, represented by processors with 2 and 4 cores on board. There is no integrated graphics chip, but some models support Turbo safe automatic overclocking mode. In any case, choosing a processor of this series, you will have to take care of a separate video card, which will incur additional costs. It can serve as a good base for low-cost gaming computers.
AMD Fusion is the most popular and very promising series. The market is represented by lines of 2-core processors with relatively low performance (they have the A4 index in the name), more productive 2-core mid-range models (with the A6 index in the name), as well as the most powerful 4-core counterparts (A8). What is noteworthy: the integrated graphics of this solution are not only better than those of competitors of a similar level, but can even outperform some low-cost video cards in terms of performance.
AMD FX is the most powerful solution that AMD has presented so far. As part of the series, 4-, 6- and 8-core solutions with a clock frequency of 2.8 to 4 GHz and higher were released to the market. The Turbo mode is implemented, the third level cache is 8 MB, the free multiplier leaves room for overclocking. Compared to Intel Core i7, it has a higher power consumption and, accordingly, heats up more, but at the same time it costs less.
For a gaming computer, it is better to pay attention to the average price range: the Intel Core i5 4670K is more than enough for modern toys, and the overclocking option will provide potential for the future; 2- or 4-core solutions for the FM2 socket ( these, for example) in conjunction with an inexpensive video card like the GeForce gtx 660 will allow you to run modern games at fairly high graphics settings.
What parameters should you pay attention to when choosing a processor?
1. Number of cores
Single-core processors execute instructions sequentially, one after the other. Multitasking is achieved through the means of the operating system - tasks are assigned a certain priority in intensity until the processor is 100% loaded. Modern processors have multiple cores, each of which boots independently. Simply put, their number characterizes the number of programs that we can simultaneously run without losing performance.
2. Clock frequency
Clock speed is the number of operations that a processor can perform per unit of time. The most important performance parameter, but not decisive. Back in the first half of the 2000s, it was really possible to determine the potential capabilities of any processor by clock frequency. Today, this parameter can only be used to compare processors of the same manufacturer, of the same architecture, and of the same family. It should also be borne in mind that for multi-core processors, the clock speed is not summed. For example, the Intel Core i5 3570K has 4 cores and a frequency of 3.4 GHz. But this does not mean at all that the processor frequency in this case is 13.6 GHz. This means that the processor has 4 cores, each of which runs at a speed of 3.4 GHz.
3. What is a cache and why is it needed?
Cache is a block of ultra-fast memory that is used by the central processing unit. If it accesses the same data over and over again, then it will store copies of them in its cache to increase performance. Modern processors have several levels of cache:
- The cache of the first level (L1) is the fastest and smallest, the volume varies between 8-128 KB;
- Cache of the second level (L2) - slower than the first, but the volume is increased to 128–12288 KB;
- The third level (L3) cache is the slowest and largest. So, for comparison, for Core i3 processors it is 4 MB, and for Core i7 - 8 or 10 MB. This is one of the reasons why the Core i7 is so many times faster.
4. Additional features
First of all, it should be noted Turboboost mode, which allows you to raise the processor clock speed when working with particularly resource-intensive tasks. This provides a performance boost - of course, strictly within reasonable limits, without the threat of damaging the chip. The function starts automatically, it can be completely disabled in the BIOS.
 |
| Turboboost - a mode of dynamic increase in the clock frequency of the processor, starts automatically when the CPU is under high load |
An important factor is the presence of integrated graphics - processors with an integrated graphics core are more expensive. Some are equipped with a powerful enough chip that can compensate for the lack of a video card in home multimedia systems. Paying attention to such solutions is primarily for those who are not going to install a full-fledged discrete video card in their computer - why pay for an integrated one if you won't use it?
An important option is the presence of an unlocked multiplier. The clock speed is the product of the bus frequency and the processor multiplier. Changing the multiplier value almost always provides additional performance. Such ones lead to an increase in heat dissipation and, in the absence of appropriate cooling, all this will, at best, end with a system freeze, at worst, with the purchase of a new processor. But as a rule, modern processors have protection against inept interference, and if the frequency is raised above reasonable measures, they overload the system and reset the multiplier value to the default. The cost between similar models with a locked and unlocked multiplier is not so significant.
Another interesting development is Intel's Hyper-Threading technology. Allows you to send two data streams to the core at the same time, while in the classic solution one core can process only one stream. Provides improved performance when working with multiple programs. Supported by Core i7 processors, as well as some i3 and i5 models.
Let's also pay attention to the "boxed" editions of processors marked BOX, which come with a basic cooling system. Many may question its effectiveness, but for the initial stage this is quite enough. The issue of price, again, is not so significant, but at the same time, boxed models are often covered by a longer warranty. If you initially plan to overlock or achieve complete silence in the computer, you need to buy better cooling. In other cases, the BOX version is likely to be the best choice.
Results
To choose the best processor for your computer, it is not enough to determine the number of cores and their clock speed. You should pay attention to belonging to a particular series, platform, set of assistive technologies, etc.
When assembling a low-cost personal computer, it is better to look at models with integrated graphics, and if the requirements change over time, you can always buy a discrete graphics card. On the contrary, if you are initially going to buy a video card, is it worth spending money on a processor with a graphics core?
Intel or AMD? Perhaps this is an eternal debate and each user individually chooses the best. At the same time, many are guided by exclusively principled views: only “red” or only “blue”. Among the objective facts, we can say that Intel is more economical in terms of power consumption, while AMD is simply cheaper with the same basic characteristics. Intel shows better compute performance in benchmarks, AMD has better graphics cores in its APUs.
Based on comprehensive statistics of the popularity of a particular model among the Internet audience.
What are the differences between the matrices, what is the response time and what screen resolution should I choose?
Solid state drives have faster write/read speeds, they are thermally stable and virtually silent.
What are the benefits of gaming mice? What is the resolution of the sensor? Is wireless worth it?
A desktop with a computer is one of the most important places in the life of a modern person.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials