Як вибрати материнську плату для ПК?
Ми незалежно перевіряємо товари та технології, які рекомендуємо.

Перше, на що варто звернути увагу, — це Socket він же роз'єм для установки процесора. Не так давно ми розповідали про процесорах (матеріал можна прочитати тут). Перш ніж перейти до вибору материнської плати, ми настійно рекомендуємо вибрати процесор. Кожна модель призначена для установки в свій унікальний роз'єм, кожна материнська плата має, зазвичай, тільки один роз'єм, відповідно, ці пристрої в чому підбираються «один для одного».
Якщо питання з процесором вже вирішене, то сміливо можете ставити галочку навпроти потрібного Socket'а в нашому підборі в колонці збоку. Це помітно скоротить кількість товарів.
Не варто також забувати, що деякі «материнки» мають вбудованим процесором, як ось ці моделі. На них варто звернути увагу, якщо необхідно зібрати простий офісний комп'ютер — особливо якщо їх необхідно кілька. Але для сучасного домашнього комп'ютера це може виявитися не найкращим рішенням.
Для яких цілей ви вибираєте материнську плату?
Для початку визначимося з завданнями, у розв'язанні яких повинен допомогти персональний комп'ютер. Як видно з колонки нашого підбору, всі представлені на ринку материнки ми поділили на 4 категорії, залежно від напрямку.
 |
|
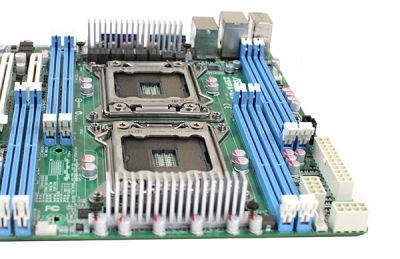
Призначені для серверів материнські плати часто обладнані двома і більше роз'ємами під процесори. Модель на фото — Asus Z9PA-D8 |
Так, якщо мова йде про класичному домашньому або офісному комп'ютері для вебсерфінгу, роботи з документными, перегляду фільмів і прослуховування музики, а також запуску не занадто вимогливих ігор, то варто придивитися до рішень цієї категорії. Відверто кажучи, це найбільш поширеним тип материнських плат, тому питання ціни коливається від невеликих 30$ до 600$. Рівень характеристик майбутнього комп'ютера — від початкового до середнього.
З ігровими «материнками» все набагато складніше. Коштують вони дорожче, виглядають агресивніше, та й функціональні можливості помітно ширше. Часто володіють хорошим доробком для розгону в майбутньому, підтримкою режимів SLI і Crossfire, прогресивним чипсетом і величезною кількістю портів на задній панелі. Якщо ви збираєтеся побудувати дійсно якісну і швидку ігрову машину, то доведеться розщедритися як мінімум на 150-200$.
Материнські плати для серверів – зовсім інша історія. Це єдині материнські плати, які дають змогу встановлювати два і більше процесорів, а також аж до 256 ГБ оперативної пам'яті. Подібні рішення забезпечують величезну обчислювальну потужність, яка в побутовому використанні виявиться абсолютно незапитаною. На них зупинятися не будемо.
Форм-фактор або розміри материнської плати
 |
| Найбільш популярні форм-фактори: ATX і micro-ATX |
Форм-фактор — світовий стандарт, що визначає розміри плати, розташування інтерфейсів, місце кріплення до корпусу та ін. Від нього безпосередньо залежить, чи зможемо ми встановити плату в конкретний корпус чи ні. Підбір по цьому параметру знаходиться в самому кінці нашого підбору в колонці збоку, оскільки він мінімально впливає на можливості самої материнки. Але визначиться з цим варто якомога швидше — це дасть змогу ще більше скоротити асортимент товарів.
Якщо у вас вже є корпус для комп'ютера, тоді спершу варто придивитися до плат відповідного розміру. Якщо корпусу немає — вибираємо форм-фактор, а після підбираємо сподобалася корпус з цього каталогу.
Найпоширенішими є варіанти ATX (305×244 мм) і його зменшена версія micro-ATX (244х244 мм). Micro-ATX оснащений 4 слотами розширення для підключення додаткових плат (відеокарта, звукова або мережева карта тощо) і може послужити відмінним рішенням для офісних ПК.
Материнські плати ATX дуже популярні серед користувачів домашніх ігрових і систем, вони володіють збільшеним числом слотів розширення, а також необхідним вільним простором для облаштування гарної системи охолодження. Ми рекомендуємо зупинитися на цьому варіанті, особливо, якщо ви збираєте свій перший комп'ютер.
Вибір чипсета або що таке "набір логіки"
 |
| Порівняння різних чипсетів від Intel |
Чипсет (також називається набором системної логіки) — це набір мікросхем, які є сполучною центром між оперативною пам'яттю, відеокартою і процесором. Часто для одного Socket виробник випускає материнки з різним набором логіки. Чим більш сучасний чипсет, тим, зазвичай, більш прогресивний список підтримки сучасних технологій.
Самими популярними і часто встановлюються на сучасні материнські плати під процесори є чипсети Intel H77 і Z77. На практиці різницю між ними зможете помітити швидше любитель сучасних комп'ютерних ігор або оверклокер. H77 — молодша модель, що забезпечує можливість розгону тільки графічного процесора, в той час як старший брат Z77 має можливість розгону процесора і оперативної пам'яті, а також підтримує режими SLI і Crossfire.
Що ж стосується рішень під процесори AMD, то тут спостерігається та сама ситуація. Наприклад, AMD 970 на відміну від старших моделей AMD 990FX і AMD 990X не володіє підтримкою декількох відеокарт у режимі SLI/Crossfire.
Тип оперативної пам'яті і кількість слотів
 |
|
DDR3 – найпоширеніший і підтримуваний всіма сучасними материнськими платами тип пам'яті |
З типом пам'яті на сьогодні все максимально ясно. Всі сучасні материнські плати підтримують DDR3, який від попередника DDR2 відрізняється збільшеною швидкістю обміну даними. Якщо у вас вже є планка пам'яті DDR2, то встановити її в сучасну материнську плату також не вийде, оскільки новий стандарт зворотної сумісності не має. Але навіть у цьому разі купувати тільки заради цієї пам'яті материнку, яка може працювати тільки з DDR2 — не найкраще рішення.
Максимальний об'єм однієї планки оперативної пам'яті становить 8 ГБ. Цього достатньо для виконання будь-яких повсякденних завдань, а також більшості ресурсномістких обчислень, 3D моделювання і сучасних ігор. Виходячи з цього, можна сказати, що користувач цілком може обійтися мінімальною кількістю роз'ємів оперативної пам'яті, що дорівнює двом.
 |
|
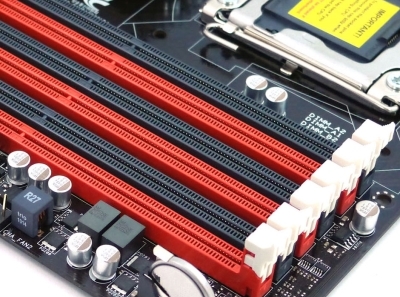
Слоти під ОЗП різного кольору ділять канали, встановлені в однакові слоти планки пам'яті будуть працювати у двоканальному режимі |
Стандартним кількістю форм-фактору ATX є 4 слота, то є можливість установки до 32 ГБ оперативки. Для любителів позамежних потужностей виробники підготували цих «монстрів», оснащених 8 слотами і більше з підтримкою чотириканального режиму роботи. Подібні девайси дають змогу встановити від 64 ГБ пам'яті, але коли звичайному користувачеві у його повсякденних завданнях може знадобитися подібний об'єм, ми сказати не беремося.
Більше увагу варто звернути не на обсяг, а на максимальну частоту ОЗП, яку в змозі підтримувати материнська плата. Чим вона вища, тим швидше швидкість роботи пам'яті. Часто серед бюджетних материнок зустрічаються випадки, коли максимальна частота «штучно занижена виробником. Так, якщо плата підтримує тільки 1600 МГц (як ці моделі), то після встановлення оперативної пам'яті на 2400 МГц (приміром, ось цих планок) швидкість роботи пам'яті все одно буде 1600. Для такої оперативки краще підібрати материнку з цього списку.
Функції/можливості сучасної материнської плати
Як ми вже говорили, материнська плата — це сполучна ланка для всього комп'ютера. У неї встановлюється процесор, відеокарта, оперативна пам'ять, накопичувачі і вся периферія. При цьому кожен елемент має свій слот підключення. Для процесора — це сокет, для внутрішнього накопичувача даних — SATA, для відеокарти, звукової карти, ТВ-тюнера, вбудованого WI-FI адаптера PCI — слот.
Сучасні материнки оснащуються слотами PCI-E x16, PCI-E x8, PCI-E x4, PCI-E x1. Кожен призначений для підключення певних комплектуючих. Зазвичай, для дискретної відеокарти відводитися верхній PCI-E x16. Що важливо: після підключення відеокарти, її система охолодження нерідко перекриває доступ до наступного PCI-слота або навіть оперативної пам'яті — зверніть увагу на розташування слота для відеокарти на фотографіях обраної материнки і розташування інших слотів стосовно нього. Фактор вільного простору дуже важливий, особливо при малих форм-факторах.
 |
|
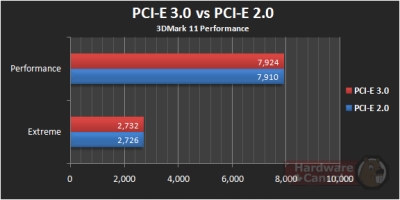
Як показують тести, різниця між роз'ємами PCI-E 2.0 і 3.0 – мінімальний або практично відсутній |
Підтримка PCI Express 3.0 з'явилася на «материнках» відносно недавно. Головна відмінність від попередника — збільшена швидкість передачі даних. Але ось неозброєним оком помітити якийсь приріст користувач не зможе, відповідно, особливого сенсу витрачати на це гроші немає. З іншого боку — в слот PCI-E 3.0 можуть встановлюватися плати і більш ранніх версій, тобто в якості покупки «на виріст» це може виявитися гарним рішенням.
На вбудований відеочип покладати особливих надій не варто, графіка інтегрована в материнку не відрізняється продуктивністю, як і вбудована графіка процесора. Такі рішення підійдуть для виконання нескладних завдань на зразок вебсерфінгу або роботи з документами.
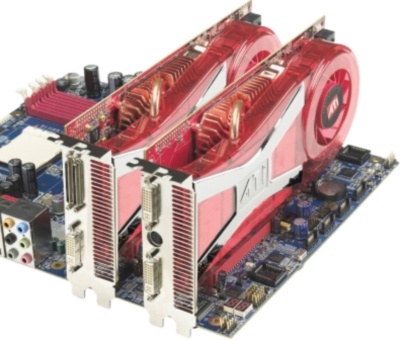 |
| Технологія CrossFire від ATI дозволяє підключати до 4 відеокарт |
Плати з підтримкою режимів SLI/Crossfire — чудове рішення для завзятих геймерів, тому що дозволяє встановити декілька відеокарт. Важливо розуміти, що наявність в материнській платі двох і більше слотів PCI-Express 16х не завжди означає підтримку цього режиму. Ось все материнки, відповідають цій вимозі.
BIOS — набір базового програмного забезпечення, «вшитий» безпосередньо в плату. У сучасних моделях вже практично не зустрінеш звичний всім БІОС з синім фоном і білими літерами на ньому. Його місце зайняв оновлений UEFI BIOS, який відрізняється зрозумілим «кликабельним» інтерфейсом, який за зовнішнім виглядом являє собою сучасну програму з безліччю додаткових можливостей.
Які роз'єми повинні бути на сучасній материнській платі?
Зазвичай, більшість сучасних материнських плат оснащені набором необхідних для роботи портів і інтерфейсів, особливо зупинятися на цьому питанні не варто. Але відзначимо кілька важливих моментів.
Для любителів неблокуються клавіатур, які використовують роз'єм PS/2, варто переконатися у наявності відповідного роз'єму на платі, оскільки в останніх моделях він відсутня або знаходиться в єдиному екземплярі для клави, або для мишки.
Якщо материнська плата підтримує роботу з інтегрованою графікою, то на ній обов'язково будуть розташовані порти VGA, DVI і HDMI. Більшість моніторів для підключення використовують DVI-роз'єм, який сумісний з інтерфейсом D-Sub (VGA) при застосуванні спеціального перехідника. Інтерфейс HDMI монітори використовують рідше, але він може виявитися відмінним рішенням для підключення до телевізора.
У сучасних рішеннях присутні як USB 2.0, та й нові більш швидкі USB 3.0. Зазначимо, що все більше сучасної техніки підключається до комп'ютера через USB: клавіатура, мишка, принтер, сканер, плеєр або планшет, тому звертаємо увагу на кількість доступних портів. Багато моделей мають більше 5 USB-портів 2.0.
Інтерфейси eSATA, Thunderbolt використовуються вкрай рідко. Варто їх брати на перспективу — складно сказати.
Звернемо увагу на материнські плати, які мають більше 3 роз'ємів для живлення кулерів. До них підключається кулер процесора, а також корпусні вентилятори, які покращують теплообмін системи із зовнішнім середовищем, видуваючи нагріте повітря та подаючи зовні більш холодний. Наявність великої кількості роз'ємів під кулери важливо для потужних систем, яким потрібне ефективне охолодження. Три кулера — це класика: на процесор, на вдув в корпус і на видув.
Роз'єм SATA3 використовується для підключення внутрішніх накопичувачів, забезпечує швидкість передачі даних близько 700 МБ/с, яку, до речі кажучи, все ще не здатні підтримувати більша частина тих же накопичувачів. Але при цьому цей інтерфейс має повну зворотну сумісність, тобто дозволяє підключати пристрої з інтерфейсом SATA2. Зворотна сумісність — це завжди добре.
 |
Заснований на комплексній статистики популярності тієї чи іншої моделі серед інтернет-аудиторії.
Повне посібників: відмінності між сокетами, ієрархія серій, значення кеш-пам'яті, кількість ядер
У чому відмінності між матрицями, що таке час відгуку і яке вибрати роздільна здатність екрану?
Твердотільні накопичувачі мають більш високу швидкість запису/читання, вони стійкі до температур і практично безшумні.
Робочий стіл з комп'ютером — одне з найбільш важливих місць у житті сучасної людини.
Статті, огляди, корисні поради
Усі матеріали

















