How to choose wheels for a car so that they are sure to become?
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

1. Type
On the shelves of auto shops you can find several types of wheel disks:
- Stamped - inexpensive steel disks, most often from the factory equipment of the car;
- Cast - wheels made of light alloys for every taste and shape;
- Forged - high-strength discs produced using hot volume stamping technology;
- Assembled - consist of a forged rim and a cast "plate", combining the advantages of cast and forged disks.
Cast wheel disks are the most widespread. They are often replaced with stamped ones, which is explained by the large variety of shapes and light weight of such products. What is the advantage? Light alloy wheels reduce the overall weight of the car, provide sensitive reactions to steering commands, and simply improve the appearance of the car.

It's up to you to decide what type of wheels to install on your car. And to make sure they fit, consider the following parameters:
- landing size (R);
- center hole size (DIA);
- number and size of mounting holes (PCD);
- disc width (J);
- wheel offset (ET);
- shape and size of fastening bolts.
2. Landing size (R)
The size of the rim circumference in " is indicated by the letter R and a number after it. This marking came from the segment of car tires.
It is not recommended to deviate from them - geometric incompatibility of wheel disks changes the parameters of the suspension and accelerates the wear of the chassis units. However, exceeding the permissible size by an " or two (provided that low-profile tires are selected correctly) usually occurs without any consequences. In this matter, it is important to study the reviews of other car owners who have already tried larger size disks.
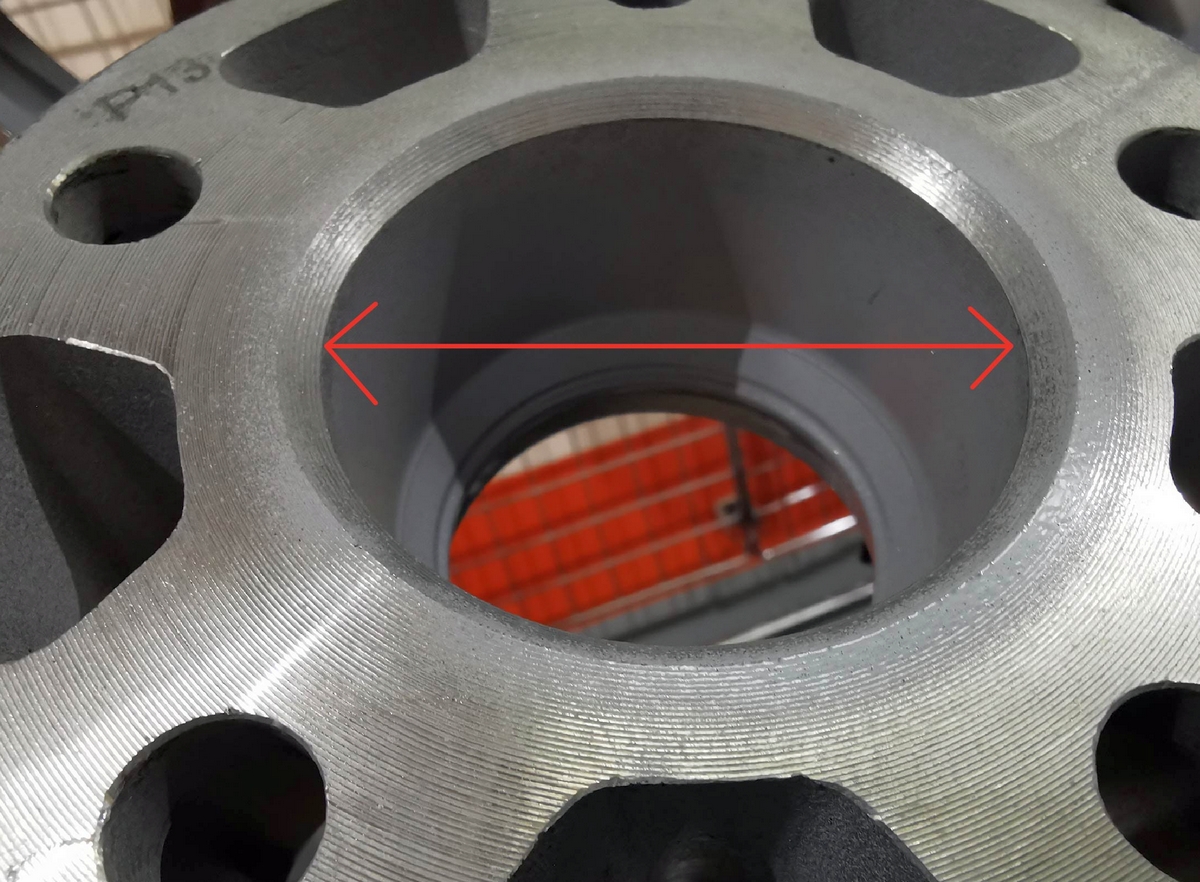
3. Center hole size (DIA)
The size of the central hole of the wheel rim is indicated in millimeters. It must correspond to the size of the centering protrusion on the car hub. Deviation of this indicator to the smaller side is not allowed, since the rim simply will not fit on the hub. If the discrepancy is to the larger side, the rim can be centered using a set of special spacer rings.
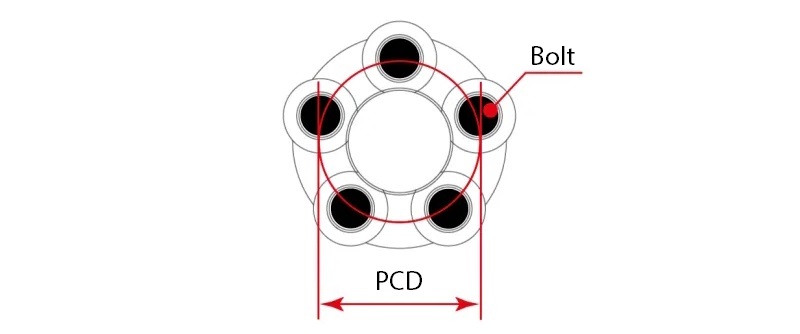
4. Number and size of mounting holes (PCD)
The PCD parameters of a wheel rim must be strictly observed. They describe the distance from the bolts or studs to the center point of the wheel, as well as the number of holes or studs on the rim. The PCD value is determined by the vehicle manufacturer and is written as a number with a multiplier.
Let's take PCD size 5x110 for example. It indicates that a rim with a size of 110 mm has 5 bolts, evenly distributed around the circumference.
5. Disc width (J)
The width of the wheel rim is measured in " and is designated by the letter J. Too wide rims can come into contact with the car's fender or its suspension components. In addition, it is the rim width parameter that influences the search filter of suitable tires - it should be 25% smaller than the tire profile width.

Using too narrow or too wide wheels is not recommended as it may result in the tire profile being out of alignment. However, small lateral deviations are still allowed: 0.5-1 " for wheels up to 15" in size and 1-1.5 " for wheels over 15".
6. Wheel offset (ET)
Wheel offset (ET) is the offset of the wheel center from the mounting point to the hub. It can be zero, positive (the hub of the wheel protrudes outward relative to the center axis of the rim), or negative (the hub is recessed inward relative to the axis).
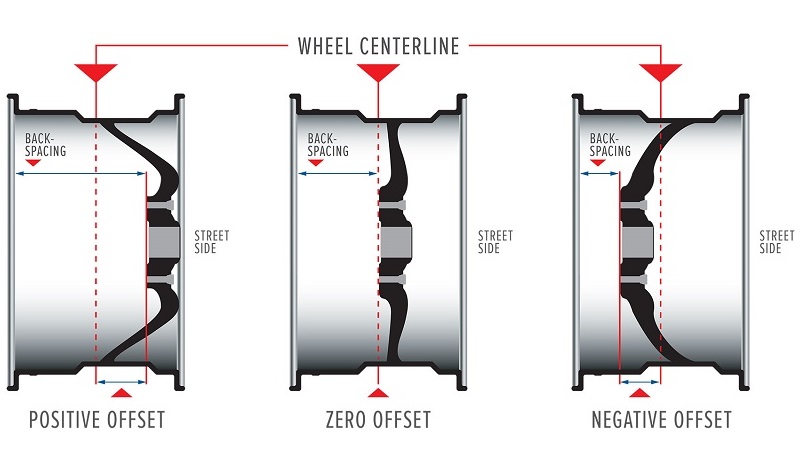
Wheels with a larger offset than specified in the vehicle's technical documentation will be located deeper inside the wheel arch, while those with a smaller offset will protrude outside the vehicle body. Wheels with an incorrectly selected offset will increase or decrease the track and may cause accelerated wear of suspension components or wheel bearings due to uneven load distribution.
7. Shape and dimensions of fastening bolts
As a rule, the working part of the bolts and nuts for wheel disks has a conical plane shape. For cast disks, bolts of increased length (due to the greater thickness of the rim) and fasteners of various shapes (with a conical, hemispherical or flat "head") are used. In order for the disks to become as they should be, this point must be taken into account.
8. Conclusion
It is best to select wheel disks by car brand - virtual search filter on the sites of large Internet resources is guaranteed to find suitable disks. Also, the parameters recommended by the vehicle manufacturer will definitely be found in the detailed operating manual for a specific car.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials























































