Inverter drive in household appliances: what is it, the pros and cons of inverter control

Inverter systems allow you to keep the heart of household appliances constantly "beating" and smoothly adjust the power, selecting it for specific needs. At a minimum, this reduces premature wear of the nodes. To save energy, inverter motors do not turn off completely — they reduce the speed when there is no need to work "to the fullest". Smooth transitions from high to low speeds are less harmful to a household appliance than constant switching on/off.
The inverter technology is based on the principle of double voltage conversion. First, the sinusoidal voltage at the input is converted to a constant, filtered and smoothed. At the second stage, positive and negative control impulses are formed from it. With their help, an alternating voltage of the required magnitude and frequency is created at the output of the converter, which is then fed to the motor. The very principle of operation of the engine does not depend on the presence of an inverter, but this additional block makes it possible to control the operation of the electric motor within wide limits.
 |
| Many famous manufacturers of household appliances do not hesitate to give an extended warranty (10 years or more) for inverter drives. |
Inverters are often included in circuits with asynchronous motors. They solve problems with high starting currents and overloads, and also allow you to change the rotation speed of the electric motor rotor from tens of revolutions per minute to several thousand. The most important advantage of this combination is the absence of a vulnerable brush assembly in the motor design, which is the hallmark of collector—type electric motors. Over time, the current-carrying brushes in them wear out and need to be replaced. The main actors of motors with an inverter drive: a rotating rotor with permanent magnets and a stationary stator with inductors. However, control circuits called inverters can be implemented in completely different ways in different devices.
We will not go deep into the technical side of the issue. It is better to focus on the advantages and disadvantages of inverter technology, as well as the features of its applicability in specific groups of household appliances.
So, let's start a comprehensive study of the qualities of inverters from refrigeration equipment:
Refrigerators and freezers
Refrigerators and freezers with a traditional linear compressor are systematically switched off when the optimum temperature in the chamber is reached. The accuracy of its maintenance varies between 3-5 °C (depends on the specific model). Each time the refrigerator motor is turned on, it experiences increased starting loads, its elements warm up, which provokes premature failure of the nodes, and the household can clearly hear the buzzing during compressor operation.
The inverter compressor takes overclocking at low speeds, gradually increasing its strength. First of all, he cools the air in the chamber to the desired temperature value, after which he slows down the pace to maintain it. The engine then works almost inaudibly at minimum rpm, then adds a little power and its measured "rumbling" can be heard. This mode is most favorable for the compressor, since it operates without starting overloads and, due to their absence, consumes less electricity.
 |
| The obvious advantages of using an inverter compressor in a hypothetical refrigerator model. |
Advantages of inverter compressors in refrigerators and freezers:
- high-precision maintenance of the set temperature in the refrigerator and freezer;
- low noise;
- no interruptions in operation and shuddering of the housing when the compressor is turned on;
- economical energy consumption (energy efficiency class A++ and higher);
- long service life (10 years warranty on the inverter drive directly from the manufacturer is quite normal practice today). Disadvantages of the inverter drive:
- sensitivity to voltage fluctuations in the power supply network (it is advisable to get a voltage stabilizer);
- the high cost of equipment and the high cost of repairing the refrigerator in case of failure.
Washing and drying machines
In the "washing machines" of previous generations, the torque is transmitted from the electric motor to the drum by means of a belt drive. The drive belt has a limited resource and, paired with current-carrying brushes, provokes increased noise, which also depends on the engine speed. Machines with inverter control are devoid of such disadvantages. In addition, they are increasingly being produced in a direct—drive layout — in models of this kind, the drum is located directly on the engine shaft.
Washing machines with an inverter motor spend less energy on rotating the drum, frequency regulation allows you to sensitively control the number of its revolutions, plus "washing machines" of this kind can boast of a quiet spin and the accuracy of setting washing modes. In drying machines, the inverter is used more for the sake of saving electricity consumption and achieving low noise during operation.
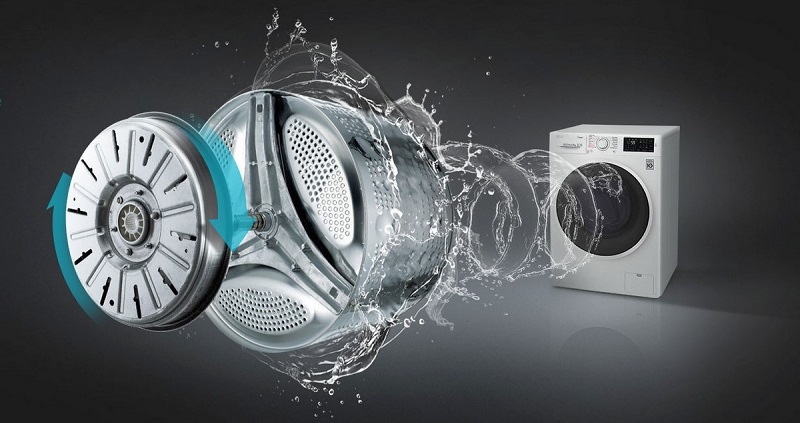 |
| "Washing machines" with direct drive are distinguished by a reduced level of vibration and noise, besides, they are many times more reliable than their peers with a belt drive. |
Advantages of "washing machines" and "dryers" with inverter control:
- improved washing quality thanks to flexible speed adjustment;
- optimal balancing by placing the drum and rotor on the same shaft;
- accuracy of setting washing modes;
- low noise level of the running motor;
- high efficiency due to the absence of friction losses;
- large operational resource;
- economical energy consumption;
- no need for maintenance of engine components.
Disadvantages of the inverter drive:
- relatively high cost of finished products;
- the complexity and high cost of repairs.
Dishwashers (freestanding and built-in)
Washing dishes is often postponed for the night hours. This is where the advantages of dishwashers with inverter control are revealed. They are notable for their low noise level (40 dB with a small "tail"), wasteful electricity consumption (they allow you to save on paying bills for light when using multi-zone metres), more efficiently work out the specified programs.
 |
| Inverter control is used in both built-in and freestanding dishwashers. |
The advantages of inverter control in dishwashers include:
- automatic determination of energy consumption depending on the load;
- low noise threshold;
- "fuel" efficiency (low energy consumption);
- a significant increase in the operational life of the equipment.
The disadvantages of the inverter drive "under the hood" of dishwashers are quite standard:
- higher price tag in comparison with odnoklassniki;
- expensive engine repairs in case of breakdowns;
- hypersensitivity to voltage surges.
Air conditioners
In inverter air conditioners, the compressor remains switched on on a constant basis, and its power changes smoothly depending on the temperature. Such climatic equipment blows not with icy air, but with air of the temperature that is needed at the moment, consumes less electricity, accurately maintains the set temperature. The inverter converter sets the speed of the compressor so that the temperature remains at the set bar. And the compressor, due to its continuous operation, does not freeze in winter.
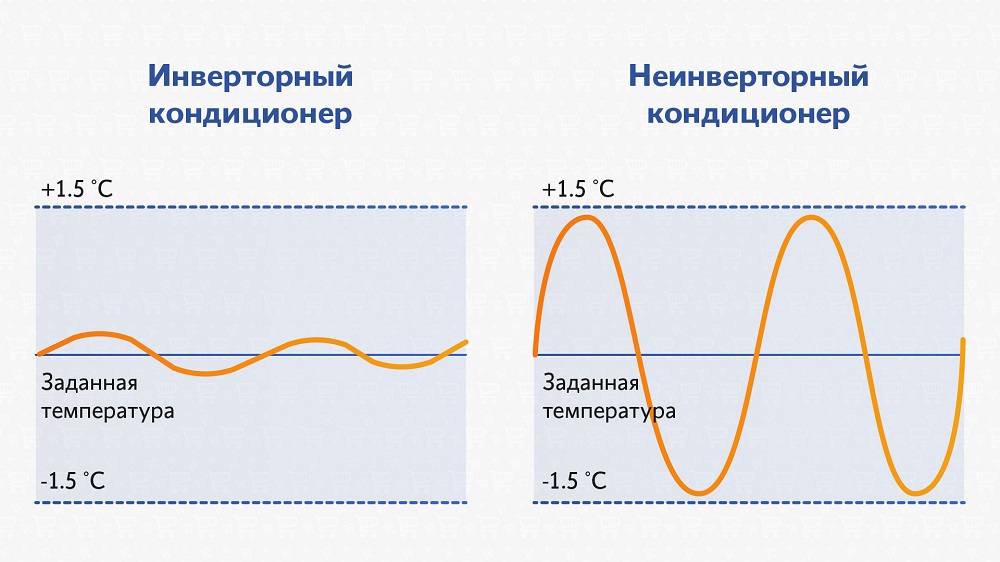 |
| Split systems with an inverter compressor are much better at accurately maintaining a given temperature regime. |
Advantages of air conditioners with inverter control:
- high-precision maintenance of the set temperature regime;
- operation at low sub-zero outdoor temperatures;
- low noise;
- low power consumption;
- durability.
Disadvantages of the inverter drive:
- the high cost of climate equipment and its repair;
- sensitivity to the quality of the power supply.
Microwave ovens
A mandatory attribute of a microwave oven is a magnetron. Often it has one fixed power, and the desired final radiation power is achieved by periodically turning the magnetron on and off. In microwave ovens with inverter control, the emitter works constantly, and its power changes smoothly depending on the selected mode. This ensures uniform heating of food and, as a result, maximum preservation of its taste qualities.
 |
| Microwaves with an inverter are quite rare "guests" on store shelves. |
Advantages of inverter control of microwaves:
- spacious inner chamber due to the absence of a bulky transformer;
- preservation of useful properties of products and improvement of taste qualities of heated dishes;
- saving time on warming up food;
- high energy efficiency;
- silent operation;
- long operational life.
Disadvantages of technology:
- high cost of final products;
- a limited range of models with an inverter drive.
The inverter can also be found on board other household appliances. So, there are electric convectors and other heaters with inverter control, vacuum cleaners and even backup power generators with an inverter. The use of an inverter drive increases the efficiency of household appliances and prolongs the life of its "hearts": turning on and off for the engine is less useful than smoothly switching from low to high speeds and back.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials















































































































