Data on Lock: Fingerprint Scanners in Smartphones
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

Fingerprint scanners as a "lock" for stored information are a convenient and secure solution aimed at protecting personal data. However, contrary to their name, they do not analyze exactly a fingerprint.
Algorithms and encryption
Instead of memorizing the branches of the papillary pattern , fingerprint scanners look for unique features and control points that determine the fingerprint's identity. The fact is that on the fingerprint, some lines branch out, others are abruptly interrupted, and others remain as separate islands. Such special points (minutiae) are the distinctive features of a specific fingerprint.
At the initial fingerprint input stage, the smartphone often asks the user to place their finger on the sensor several times, moving it slightly to the sides. This procedure is necessary to remember the largest number of minutiae. The more unique features the scanner sees, the more analysis points it will have at its disposal.
 |
| Fingerprint scanners do not remember the fingerprint itself, but rather the characteristic points in it. |
Orientation to control points gives a much better effect than banal memorization of papillary pattern. Judge for yourself, small cuts of the pads, applying the finger at different angles and with different pressure, and simply a greasy coating on the fingers after eating a station cheburek change the scanning picture. But minutiae always remain unchanged.
Today, smartphones use three types of fingerprint scanners: capacitive, optical and ultrasonic.
Capacitive
Capacitive fingerprint scanners identify a finger using electricity. They are constructed from a series of tiny conductive plates with capacitors that store specific charges. When a finger is placed on the fingerprint, the ridges of the fingerprint change the stored charge where the fingertip touches the conductive plates. Conversely, air gaps are created in the valleys of the fingerprint, leaving the capacitor charge relatively unchanged.
The smartphone reads all the cells on the surface of the fingerprint scanner and determines by the voltage whether there was a void near a specific capacitor or whether it was a ridge where the skin touched the sensor. This is how a three-dimensional picture of the fingerprint is formed, taking into account the protrusions and depressions on the finger.
 |
| Visualization of the operating principle of capacitive fingerprint scanners. |
It is quite difficult to fool capacitive fingerprint scanners. They are characterized by high stability of operation, easily recognize wet and dirty fingers. Smartphones of various ranks use capacitive sensors with different resolution: budget hand models are equipped with scanners with a small number of cells, while mid-range and flagship devices have multi-cell sensors. The more capacitors in the scanner design, the more accurate the "map" of ridges and depressions it sees thanks to electrical signals, which increases the level of scanning security.
Advantages of capacitive fingerprint scanners:
- creation of a three-dimensional image during scanning;
- high response speed;
- excellent security;
- stability of operation (the finger does not necessarily have to be dry and clean);
- low cost production.
Disadvantages of capacitive fingerprint scanners:
- low resolution in budget smartphone models;
- the impossibility of installing a scanner in displays (screens on mobile devices are also capacitive, which is why the technologies overlap with each other).
Optical
Optical scanners use light to detect a suitable fingerprint. They are essentially a black and white camera that takes a photo of the finger pad and analyzes the papillary pattern based on the lightest and darkest areas of the image. The pattern is illuminated during scanning with many tiny diode lamps so that the sensor can “see” better and small details can be read from the finger.
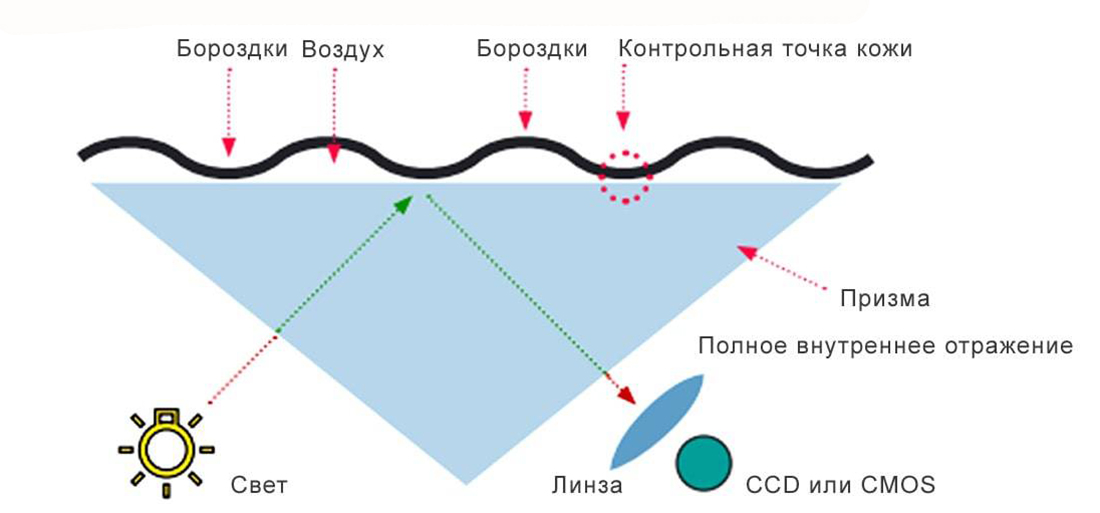 |
| Optical sensors "photograph" the fingertip with a flash. |
Optical fingerprint sensors provide a two-dimensional image, which makes them easy to fool. Such scanners are usually installed directly into the screen of mobile devices. However, only translucent AMOLED and OLED panels are suitable for them. In the case of a traditional IPS matrix, the sensor camera clutters the backlight, which is located in the rear plane of the screen.
Advantages of optical fingerprint scanners:
- Possibility of installation directly into the screen.
Disadvantages of optical fingerprint scanners:
- two-dimensional scanning, which makes it easy to fool optical scanners (attach a dummy or fake with the desired fingerprint);
- not the best recognition stability (dirt and water greatly affect fingerprint detection algorithms);
- low operating speed (especially in early versions of the technology);
- picky about protective films and glass.
Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic scanners are the "youngest" type of fingerprinting. The well-known company Qualcomm, which produces mobile processors for smartphones, had a hand in developing the first versions of such sensors. The debut of the ultrasound scanner took place on board the flagship Samsung Galaxy S10 in 2019. However, a couple of years before this event, a prototype of the sensor was "tested" in the LeTV Le Max Pro phone.
The ultrasound scanner is based on a piezoelectric material. When voltage is applied, it begins to vibrate at a high frequency and generates sound waves that pass through the protective glass of the smartphone, “hit” the recesses and protrusions of the fingerprint, and then return back to the scanner. The result of the measurements is the determination of the intensity of the reflected ultrasound pulse at various points of the sensor, which results in a detailed three-dimensional picture of the finger pad.
 |
| Ultrasonic sensors emit sound waves to identify the owner of a smartphone using a fingerprint. |
Ultrasonic pulses penetrate a little deeper into the finger, which means that you won't be able to slip a fake one into the smartphone. Such scanners are excellent at distinguishing real fingers from imprints. And moisture and dirt are not an obstacle for them.
Advantages of ultrasonic fingerprint scanners:
- 3D scanning;
- high security;
- effective protection against all kinds of dummies;
- stability of operation (the finger does not necessarily have to be dry and clean);
- the ability to be placed anywhere (under the glass, on the “back” of the smartphone, in the side power button).
Disadvantages of ultrasonic fingerprint scanners:
- Ultrasound scanners are slower than others;
- sensitivity to protective films and glass (some of them scatter and partially dampen the sound wave).
Where are they located?
In their early days , fingerprint scanners were often placed in the Home button, which was installed on the chin below the screen. Front fingerprint sensors are a distinctive feature of the Apple iPhone (starting with the 5s generation), the first Samsung Galaxy S models, and other mobile devices from the recent past.
 |
| In Apple smartphones, the Touch ID unlocking system has been used since the iPhone 5s model. |
As the technology became more widely available, fingerprint sensors migrated to the back of smartphones. Rear scanners are still common today. This placement is the prerogative of inexpensive mobile phones.
The under-screen fingerprint scanner first made its way into the spotlight at the beginning of 2018. The Vivo X20 Plus UD model was equipped with such a sensor. The technology quickly gained popularity and many reputable smartphone manufacturers began to integrate a fingerprint scanner into the screen. At first, only flagship devices were equipped with such a scanner, but now you can find it in many solid mid-range smartphones with AMOLED or OLED displays.
 |
| In-screen fingerprint scanners are no longer the preserve of flagships and have migrated to the mid-range smartphone segment. |
Recently, there has been a tendency to place the fingerprint scanner on the surface of the side power/unlock button of phones. The main advantage of such a location is the neat appearance of the case and the inconspicuousness of the sensor itself.
A few words about iPhone
Oddly enough, the iPhone was one of the first mass-market smartphones with a fingerprint scanner, but it has long been absent from the modern portfolio of Apple mobile devices. The fingerprint scanner was abandoned in the revolutionary Apple iPhone X model, replacing the sensor with Face ID face unlocking.
 |
| Face ID is the primary authentication method for iPhone owners. |
If you dig a little deeper, the iPhone's fingerprint sensor worked just fine, but in terms of repairability, it was a downright weak point of Apple smartphones. Repairing a broken Touch ID is a virtually hopeless endeavor, since it usually entailed replacing the system board.
Fingerprint scanners have become a simple and secure alternative to countless passwords and patterns. The technology has room to develop further, and widespread penetration into mobile payment systems makes fingerprint sensors an important security tool for the future.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials





























































































