How to choose a power supply for a PC

In the catalog you can find a large assortment of power supplies to choose the right model for your PC.
What criteria should you consider when choosing a power supply for your home and gaming PC?
When choosing a power supply, you must consider the purpose of the computer. Home and office PCs are rarely subjected to increased loads, and entry-level components are sufficient to perform basic tasks (searching for information on the Internet, watching movies, working with documents, amateur photo and music processing). For stable operation, any inexpensive power supply will suffice, and in some cases you can take a case with a complete power supply.
Gaming machines will require a more careful approach. The power supply must not only be of high quality, but also easy to install and efficient in operation under load. Protective mechanisms play a key role and will help maintain the integrity of other components (motherboard, processor, RAM, video card) in the event of overload, power outages and other emergency situations.
Depending on the purpose of the computer, the following criteria for choosing a power supply can be distinguished:
| Home/Office PC | Gaming PC |
|---|---|
| general power | general power |
| Basic control systems | Basic and additional control systems |
| Availability of necessary connectors | Certification level 80+ |
| Noise level | Presence of PFC |
| Form factor | Cooling efficiency |
| Noise level | |
| Cable connection type | |
| Availability of necessary connectors | |
| Form factor |
How much power supply power is required for stable computer operation?
There is no point in saving on the power supply, but it is necessary to select it with a power reserve. The indicator is determined based on the installed components, so the choice of power supply is carried out at the end to ensure stable operation of the entire assembly. Let's look at the example of a mid-range PC:
| Accessories | Consumption, W | Total PC consumption, W |
|---|---|---|
| Asus ROG STRIX B760-F GAMING WIFI motherboard | 60 | 345 |
| Processor Core i5-12600K | 150 | |
| Video card MSI GeForce RTX 4060 VENTUS 2X BLACK 8G OC | 115 | |
| RAM Kingston Fury Beast DDR5 RGB 2x16Gb | 15 | |
| Deepcool AK620 Zero Dark CPU Cooler | 2 | |
| Case fans Deepcool FK120-3 IN 1 | 6 | |
| SSD Kingston KC3000 SKC3000S/1024G | 5 | |
| Additional lighting | 2 |
The resulting figure of 345 W is nominal and represents power consumption in normal mode. The power dispersion between PCs during rest and load is quite large, so it is important to take this factor into account. When running games and resource-intensive applications, the computer will need about 40% more. The main consumers are the processor and video card, so it is recommended to study their characteristics well to ensure normal operation in any mode. Having made some simple calculations, we already get about 480 W, but now it is necessary to provide a small power reserve. The fact is that the power supply can, of course, operate at the limit of its capabilities, but the service life will be shorter, and there is a risk of damaging not only it, but also other components. We add another 20–30% reserve, we get a final figure of about 600 W. The power reserve will prevent overheating, overload and system failures. The cooling fan will not accelerate to maximum, which means the noise will be minimal.
If you don’t want to bother with calculations, then you can safely take a 450 W power supply for budget home and office builds (up to Core i3 / Ryzen 3 processor and integrated graphics). The 600 W option will be enough for a PC with a Core i5 / Ryzen 5 core and an entry-level video card, for example, Palit GeForce GTX 1650 GP OC or even an average MSI GeForce RTX 3060 VENTUS 2X 8G OC. For professional gaming systems, it makes no sense to consider models less than 800 W, since only graphics adapters will require 300+ W of power.
Primary and secondary self-control systems
Monitoring the input and output parameters of the power supply (current, voltage, temperature, resistance) allows you to respond to changes in a timely manner and prevent the negative consequences of failures. There are standard safety mechanisms that are present in all power supplies:
- Overall Output Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
- Output Overcurrent Protection (OPP)
- Short Circuit Protection (SCP)
This set is sufficient for most home and office PCs, but the response threshold can be quite large and destructive for some components, so it would not be superfluous to install a UPS. Additional control tools will help increase the safety of operation of the system unit:
- Overload protection on individual power outputs: 3.3V, 5V and 12V (OCP)
- Output Under Voltage Protection (UVP)
- Overheat protection of the most vulnerable components (OTP)
- Surge Protection (SIP)
When assembling a gaming computer, it is better to make sure that the listed systems are available and take a high-quality power supply. It will cope with sudden voltage changes and possible network outages, provide effective monitoring of the status of individual supply lines, and will not create interference.
Which 80 PLUS certification should I choose depending on the purpose of my PC?
80 PLUS certification dates back to 2003–2005 and remains an indicator of high energy efficiency of a power supply. It displays the coefficient of performance (COP) that the device can provide at different load levels - 20% / 50% / 100%. You can see the effectiveness of standards at different levels in more detail in the table:
| Certificate | Load 10% | Load 20% | Load 50% | Load 100% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 PLUS (White) | — | 82 | 85 | 82 |
| 80 PLUS Bronze | — | 85 | 88 | 85 |
| 80 PLUS Silver | — | 87 | 90 | 87 |
| 80PLUS Gold | — | 90 | 92 | 90 |
| 80PLUS Platinum | — | 92 | 94 | 92 |
| 80 PLUS Titanium | 90% | 94 | 96 | 94 |
The higher the "precious" standard, the better the power supply will perform, but the price will also increase. You can study the features of certificates in a separate article. In general, for budget PCs that are rarely subjected to high loads, the basic White or Bronze is sufficient. If you want additional guarantees of high performance when building a PC for mid-range gaming, then choose Silver or Gold. The 80+ Platinum certification is suitable for professional gamers and servers. Titanium is an expensive prerogative of enthusiasts who engage in overclocking and comprehensive testing of hardware.
What is PFC and how does it affect energy supply?
PFC (Power Factor Correction) is power factor correction. Simply put, this is a module that equalizes the voltage supplied to the power supply. Deviations in the power supply are not a rare occurrence, so most manufacturers include one type of PFC in the power supply circuit - active or passive. The latter is not very common, since it does not provide high efficiency with significant voltage drops. Active correction based on the controller, inductor and power components can increase the efficiency of the power supply up to 96% and ensure stable operation with an input voltage in the range of 160 - 280 V. When choosing a power supply, you must make sure that PFC is present, since its absence leads to negative consequences:
- Increased heating of electronic components
- Increased load on the transformer
- Deviation of current output parameters, which leads to the activation of protective mechanisms
- The occurrence of interference in the electrical network
Efficiency and useful functions of the cooling system
During operation, the power supply inevitably releases thermal energy, the amount of which increases in proportion to the load. An active cooling system in the form of fans allows you to maintain the optimal temperature of electronic components and is mandatory. The exception is power supplies with passive technology, found in premium models with Titanium certification.
To ensure a good balance of efficiency and noise, it is necessary to select sources with 120 - 135 mm fans that do not need to spin up to maximum to create a powerful air flow. Options with an 80 mm turntable remain relevant only for budget and non-standard (narrow) power supplies. Semi-passive cooling, similar to PWM CPU coolers, is considered a popular trend. Such devices regulate speed depending on the readings of the temperature sensor, which allows you to achieve absolute silence when there is no load.
Type of cable connection and set of required connectors
The type of cable connection affects the ease of assembly, connection quality and aesthetics of the system unit. The most popular option is the classic non-removable arrangement by soldering wires directly to the power supply board. It guarantees the best contact and eliminates excessive heating at the joints.
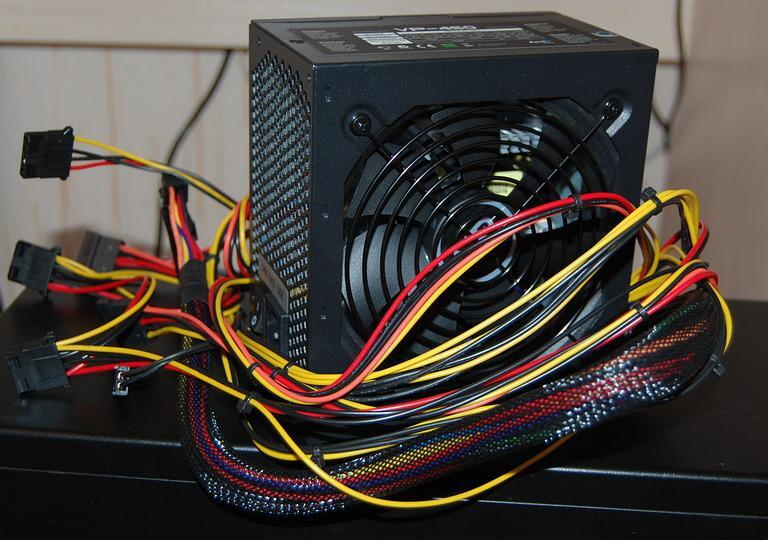

The second most popular is the modular (removable) design, which allows you to use only the necessary power lines and get rid of “hanging” wires. This approach is more convenient during computer assembly, allows you to organize competent cable management, but is a little more expensive.
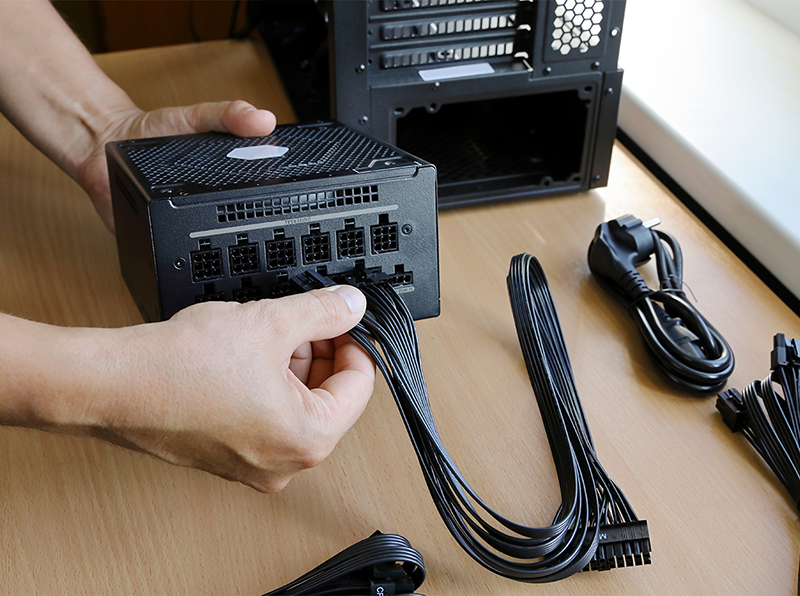

Manufacturers also offer semi-modular power supplies that combine the advantages of both types. The implementation may vary, but most often the base power lines for the motherboard, hard drive and SSD, as well as some fans (Molex), remain non-removable. Modular cables are used for the main and additional power supply to the processor and video card.

When choosing a power supply, it is very important to provide the necessary connectors for connecting to the components. The set may vary depending on the assembly:
- For powering the processor: 4, 6, 8 pin, as well as various combinations
- For powering the video card: 6, 8, 16 pin and their combinations
Connectors for the motherboard (20+4 pin), hard drive / SSD (SATA), fans (Molex) are standard and are present in sufficient quantity by default.
Advice! For gaming PCs where components require additional power, it is better to choose a power supply with independent lines to ensure connection according to the following scheme:
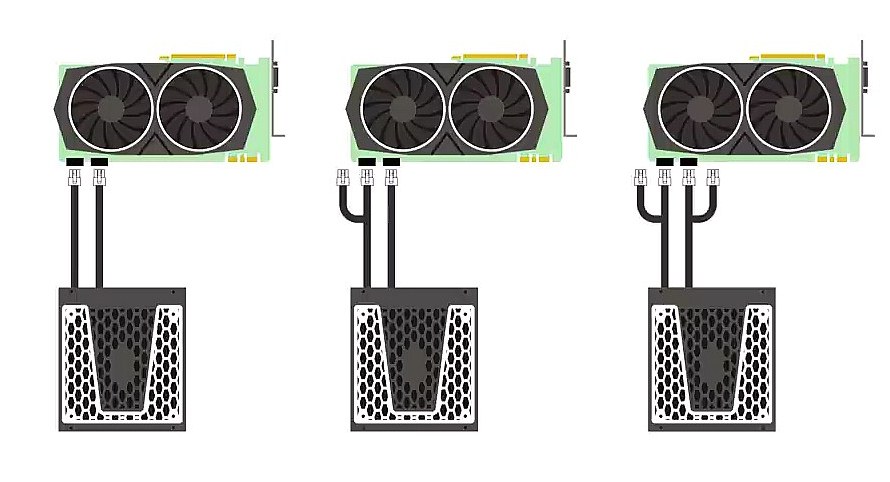
This will avoid overheating and overload on individual channels.
How to choose the right PSU form factor?
There are three form factors of power supplies that correspond to certain types of cases:
- ATX : the most common type, compatible with Mini, Midi, Full, Ultra Tower, Desktop and Cube Cases. Width 150 mm, height 86 mm.
- TFX : Non-format desktop version. It stands out for its small width of 85 mm and height of 65 mm.
- SFX : A smaller version of ATX for compact builds in Mini Tower, Desktop and Cube Cases. Width 125 mm, height 64 mm.
Important! Regardless of the order of selection of components (PSU - case or case - PSU), make sure that not only the standards are compatible, but also the depth, which can be different. Fixed HDD cages and miniature system units limit space and impose certain restrictions on the dimensions of power supplies.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials


































































