How to Properly Store Charging Stations, Power Banks, Batteries, and Generators
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

1. Charging Stations
Portable Charging Stations — this is battery equipment for ensuring energy independence. Accordingly, key requirements for storing such equipment are placed precisely on the battery.
Where and How to Store
In a dry and cool place, away from heat sources and direct sunlight. This can be a pantry in an apartment or country house, a wardrobe, etc. However, a balcony is not the best choice for storage.
Be sure to avoid damp conditions, low (negative) and high temperatures — temperature fluctuations negatively affect the battery, and with regular temperature changes, condensation can form inside the device. As is known, moisture is detrimental to electronics.
It makes sense to place the charging station in a box or case (if available) — this will protect the equipment from dust and dirt, which potentially leads to clogging of vents and connectors. Regarding ports — it is advisable to disconnect all cables and adapters from them (to avoid damage).
What Charge Level to Maintain
Maintaining the optimal charge level of the battery is the key to the long-term functioning of the charging station. Before putting it into long-term storage, be sure to check that the battery is not completely discharged. It is best to adhere to the "30 – 70" strategy, i.e., keep the battery charge within 30% to 70%. A discharged or fully charged battery will lose its capacity more quickly.
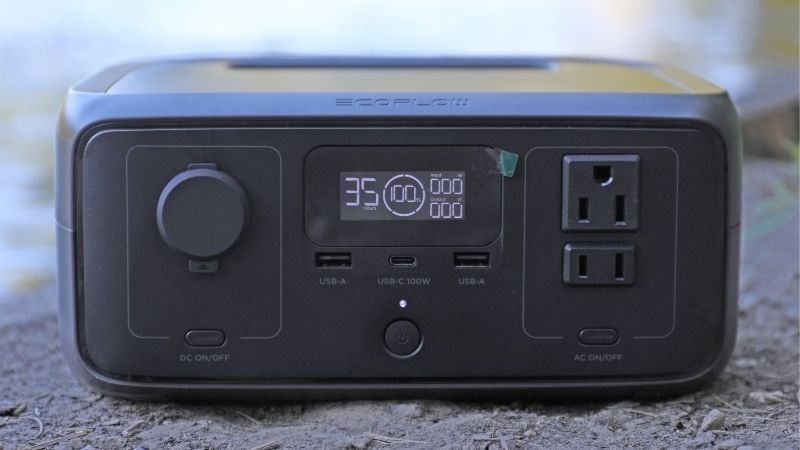

Make it a rule to check the battery status at least once every 3 months. Recharge the battery if necessary to keep it operational. For example, the company EcoFlow recommends for most of its products to discharge the battery to about 30% and then immediately charge it to 60% — this action algorithm should be repeated every 3 months. A detailed guide on specific models of charging stations from this manufacturer is presented at the link.
2. Powerbanks
Powerbanks are expected to be stored similarly to charging stations — the equipment operates on similar principles and essentially differs only in size (along with more advanced management algorithms for portable charging stations).
Where and How to Store
At room temperature, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Also, avoid high humidity: the bathroom is certainly not the best place for storing a powerbank. Naturally, keep the Powerbank battery clean, to prevent dust and other contaminants from getting inside its casing.

What Charge Level to Maintain
The powerbank battery charge needs to be maintained at medium percentage values. The above-mentioned "30 – 70" tactic will do, ideally even "50 – 70". This charge level is considered favorable for maintaining the correct chemical balance inside the battery. In this case, self-discharge will occur more slowly, and the risks of battery degradation are minimized.
3. Batteries
As a rule, the storage features of batteries are specified in the user manual or manufacturer's instruction — this information should be the main point of reference. Certain types of batteries may have their own specific requirements, so we can only provide general storage recommendations.
Where and How to Store
In a dry, cool, shaded place with good ventilation. The optimal storage temperature is from 0 °C to 25 – 40 °C (depending on the specific type of battery).
Automotive lead-acid batteries SLA and EFB should ideally not be stored in residential premises, as such batteries emit harmful fumes. Suitable for closed premises are gel, absorbent glass mat (AGM), and lithium battery types (in particular, Li-Ion and LiFePO4).
The battery must be protected from any mechanical impacts, the device should be disconnected from the charger and consumers. The battery is supposed to be placed horizontally and no other way.
What Charge to Maintain
Long storage of batteries in a fully charged or discharged state leads to loss of capacity and reduced performance. Lithium batteries are recommended to be stored charged approximately halfway, AGM, and gel batteries — charged up to 80%.
If your setup involves using a car battery along with an inverter, regularly check the voltage of the battery — it should be within the range of 12.4 – 12.7 V. And if the voltage has dropped to 12 V or below, it is essential to recharge the battery. Otherwise, sulfation of the conductive plates may begin, leading to failure (this is relevant for lead-acid batteries).
4. Generators
Generators are another kind of equipment for ensuring energy independence. They require a more meticulous approach.
Where and How to Store
Household generators with an open design are supposed to be stored in dry rooms with an air temperature above zero and good ventilation. Close to them, there should be no barrels of water, containers with acids and alkalis, and no battery storage is allowed nearby. The device should preferably be covered with a suitable cover.
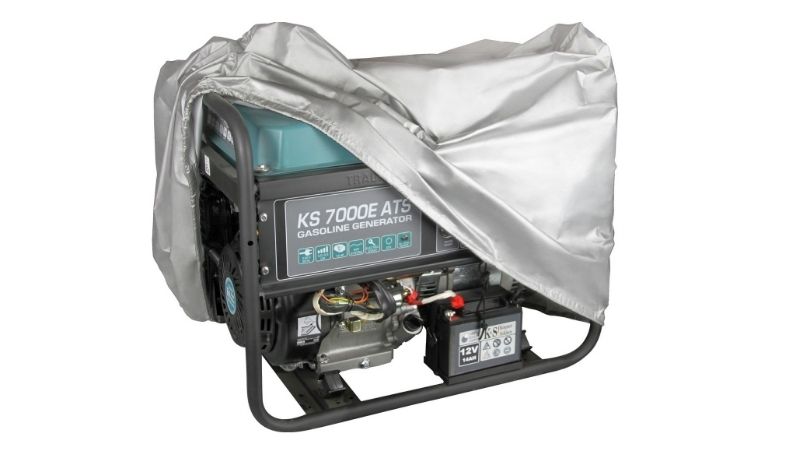

Large models of generators may often be designed in all-weather containers. They can be stored outdoors. Compact inverter generators are often made in a casing. They are better stored indoors, but without additional cover.
If you are certain that the generator will not be used for an extended period, it is worth correctly preserving the equipment.
How to Properly Preserve the Generator
Preservation is needed when the generator is used seasonally. For example, only during the summer at a cottage or exclusively in the winter for heating systems. That is, the unit regularly operates for 3 – 4 months, and the rest of the time it is idle.
Preservation recommendations are usually presented in the technical documentation for a specific generator model. But the general procedure is as follows:
- use fuel preservatives or completely drain the fuel from the tank and fuel system — for the latter, it's enough to shut off the fuel valve on a running unit and wait until all the gasoline is used up and the engine stalls itself; in diesel generators, fuel draining is not necessary, but it's crucial to monitor fuel seasonality — if summer diesel is left in the system for winter, it will wax and clog the filters;
- change the engine oil (even if the deadline for scheduled oil replacement has not yet come);
- clean and replace spark plugs (if necessary);
- clean or replace the air filter;
- plug the fuel filler neck in the tank (to prevent moisture — the main source of corrosion processes — from getting inside);
- seal the exhaust pipe with an oiled rag plug;
- remove or disconnect the battery (for models with electric start function);
- check the integrity of the construction and connections, clean the unit from contaminants, repaint it (if necessary).
Additionally, it's recommended to pour a couple of dozen grams of engine oil into the cylinder, having previously removed the spark plug. Afterward, it’s necessary to pull the recoil start rope a few times — the oil will spread across the cylinder and piston rings, providing lubrication for these assemblies and protection against corrosion.

Conducting preservation activities takes minimal time and prevents equipment failure at the start of the season.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials

















































































