Як вибрати дитяче автокрісло
Ми незалежно перевіряємо товари та технології, які рекомендуємо.

1. Вагові групи
Починати пошук оптимальної моделі необхідно з визначення відповідної групи, а для цього потрібно знати вік, вагу та зріст дитини:
0+ (до 13 кг)
Автолюлька-переноска для найменших – новонароджених немовлят вагою до 13 кг (приблизно до 12-15 місяців). Вона встановлюється виключно проти ходу руху, оскільки у малюка ще недостатньо зміцнілий хребет, а удар або різке гальмування призведуть до ривків головою та надмірних навантажень на шию та спину. Спинка та сидіння забезпечують правильне розташування немовляти в позі напівлежачи, внутрішні ремені гарантують надійну фіксацію, а напівкругла основа дає змогу заколисувати малюка, як у колисці. Найчастіше автокрісла цієї групи оснащені м'яким вкладишем, який можна зняти та випрати, ручкою для перенесення та захисним козирком від сонця. Завдяки підтримці хребта та правильному розташуванню новонароджений може подорожувати в такій автолюльці тривалий час.
0+/1 (0-18 кг)
Мультигрупа автокрісел є універсальним варіантом для дітей з перших днів життя та приблизно до 4-річного віку (або, точніше, до 18 кг). Вона відрізняється від групи 1 наявністю спеціального вкладиша для немовлят, який згладжує кут посадкового місця та розподіляє навантаження на хребет дитини, уникаючи тиску на куприк. Первинно ці крісла встановлюються проти руху, а в міру дорослішання пасажира їх можна повернути по ходу руху. Більш прогресивні моделі мають можливість обертання на 360 градусів – тобто ви можете крутити сидіння в будь-якому напрямку залежно від обставин, не переставляючи крісло. Перевагою таких пристроїв є ширший діапазон використання та, відповідно, економія коштів, які могли бути витрачені на купівлю різних автокрісел.
0+/1/2 (0-25 кг)
Ще універсальніша група, яка поєднує в собі можливості типів 0+, 1 та 2 та призначена для дітей від народження до молодшого шкільного віку (приблизно до 7 років або до 25 кг). Такі автокрісла мають вкладиш для правильної підтримки хребта новонародженого і встановлюються первинно проти ходу руху, а потім — у зворотному напрямку.
0+/1/2/3 (0-36 кг)
Найуніверсальніша комбінована група прослужить вам з перших днів життя малюка до 12 років, тобто весь час, коли взагалі існує потреба у спеціальному підтримувальному пристрої для маленького пасажира. Варіанти «все в одному» мають гнучкі можливості регулювання нахилу спинки та підголівника для забезпечення комфортних умов і для найменших, і для дітей, що підросли. Такі крісла досить громіздкі та важкі, зате дають змогу значно заощадити і не турбуватися про своєчасну купівлю моделі необхідної групи.
1 (9-18 кг)
Автокрісла, розраховані на дітей віком від 9 місяців до 4 років, зростом від 80 до 105 см та вагою від 9 до 18 кг. Простіше кажучи, на такі моделі можна переходити, коли дитина впевнено тримає спинку і вже сидить. Як правило, спинка тут регулюється в декількох положеннях для комфортного сну та активності, але до лежачого положення не опускається – це небезпечно під час їзди. Крім того, такі автокрісла можна встановлювати по ходу руху та проти нього.
1/2 (9-25 кг)
Мультигрупа, що поєднує у собі можливості типів 1 і 2 і призначена для дітей віком від 9 місяців до 6-7 років або вагою від 9 до 25 кг.
1/2/3 (9-36 кг)
Універсальні моделі, що підходять під параметри груп 1, 2 та 3. Користуються великою популярністю, оскільки призначені для дітей віком від 9 місяців до 11-12 років (або вагою від 9 до 36 кг). Такі автокрісла мають власні ремені безпеки, які в міру дорослішання пасажира відстібаються, і дають змогу регулювати спинку та підголівник для створення комфортних умов для малюка та дорослішої дитини.
2/3 (15-36 кг)
Автокрісла для дітей віком від 3 до 12 років, які позбавлені власних ременів безпеки та мають широкий діапазон регулювання підголівника. Дитина фіксується штатним ременем безпеки, а самі крісла встановлюються лише під час руху автомобіля.
3 (22-36 кг, бустер)
У більшості випадків це не повноцінне крісло, а сидіння-підкладка, що не має спинки та бічного захисту, з твердою основою та підлокітниками. Хоча існують також бустери з невисокою спинкою. Це пристрої для дітей віком від 6 до 12 років, головна задача яких –трохи підняти пасажира і таким чином забезпечити правильне розташування штатного ременя безпеки (через середину плеча та грудей, а не по шиї). Водночас від бічних ударів бустери не захищають.


Для зручності сприйняття ми об'єднали всі дані про вагові групи в таблицю:
| Вагова група | Вага | Зріст | Вік | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Основні групи | 0+ | 0-13 кг | 40-85 см | від народження до 15 місяців |
| 1 | 9-18 кг | 80-105 см | з 9 місяців до 4 років | |
| 2 | 15-25 кг | 100-135 см | від 3 до 7 років | |
| 3 | 22-36 кг | 125-150 см | від 6 до 12 років | |
| Комбіновані групи | 0+/1 | 0-18 кг | 40-105 см | від народження до 4 років |
| 0+/1/2 | 0-25 кг | 40-135 см | від народження до 7 років | |
| 0+/1/2/3 | 0-36 кг | 40-150 см | від народження до 12 років | |
| 1/2 | 9-25 кг | 80-135 см | від 9 місяців до 7 років | |
| 1/2/3 | 9-36 кг | 80-150 см | від 9 місяців до 12 років | |
| 2/3 | 15-36 кг | 100-150 см | від 3 до 12 років | |
2. Типи кріплень
Правильно підібране дитяче автокрісло ще не запорука успіху, адже безпека також залежить від кріплень і правильності встановлення. Існує три основні типи кріплень автокрісел.
Штатні ремені безпеки
Найбільш простий та універсальний спосіб, тому що є в будь-якому сучасному автомобілі. В автокріслах для маленьких дітей (до 4 років) додаткові кріплення не потрібні, тому що сам пристрій закріплюється за допомогою ременя, а малюк фіксується окремими три- або п'ятиточковими ременями, якими оснащено крісло. Моделі для старших дітей, у тому числі бустери, залишаються на місці під вагою пасажира, а вже сама дитина пристібається ременем безпеки.

ISOFIX
Система, запропонована Міжнародною організацією зі стандартизації ISO у 1990 році з метою зробити встановлення дитячих автомобільних крісел максимально надійним, простим та швидким. Для цього і на автокріслі, і в машині мають бути спеціальні скоби – по парі вбудованих металевих замків, які замикаються між собою. Така система вважається найбільш надійним кріпленням та зводить до мінімуму можливість неправильного встановлення. Тим більше, багато моделей доповнено індикацією – маркуванням, яке змінює колір у разі встановлення автокрісла належним чином.
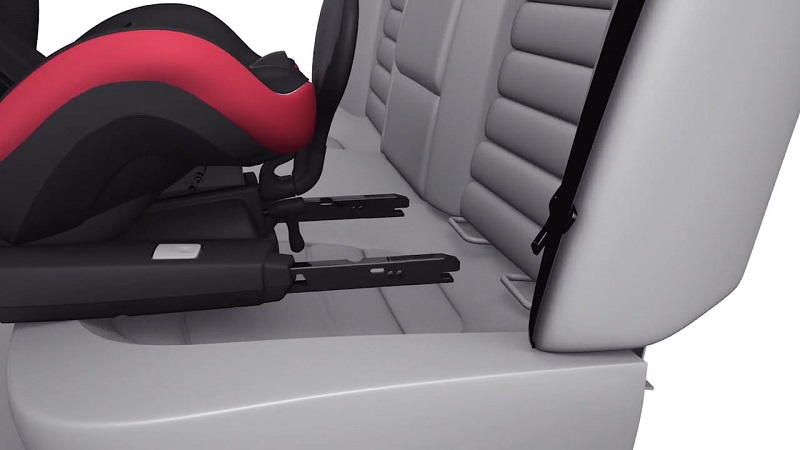

Кріплення ISOFIX є в базовій комплектації багатьох сучасних автомобілів, особливо в Європі. Зазвичай, місця розміщення кріплень в авто позначаються пластиковими напрямними, прапорцем з відповідним написом або пластиковим значком. Іноді кріплення заховано під обшивкою. Фіксатори здебільшого є на двох крайніх сидіннях ззаду, хоча є машини із системою ISOFIX на передньому або на всіх пасажирських місцях. Крім цього, є автокрісла, які кріпляться лише за допомогою автомобільного ременя, інші – поєднують його з ISOFIX, треті – лише за допомогою ISOFIX-замків. Деякі моделі комплектуються спеціальною базою ISOFIX, на яку встановлюється саме крісло.
Важливо наголосити, що система витримує навантаження до 18 кг. Тому автокрісла для старших дітей та бустери комбінують ISOFIX та кріплення за допомогою штатного ременя безпеки.
Latch
Аналог ISOFIX, спеціальні кріплення, які переважно зустрічаються в американських марках автомобілів і обов'язкові в Штатах з 2002 року. Вони також передбачають спеціальні замки, які фіксують автокрісло в нижній і верхній частинах.
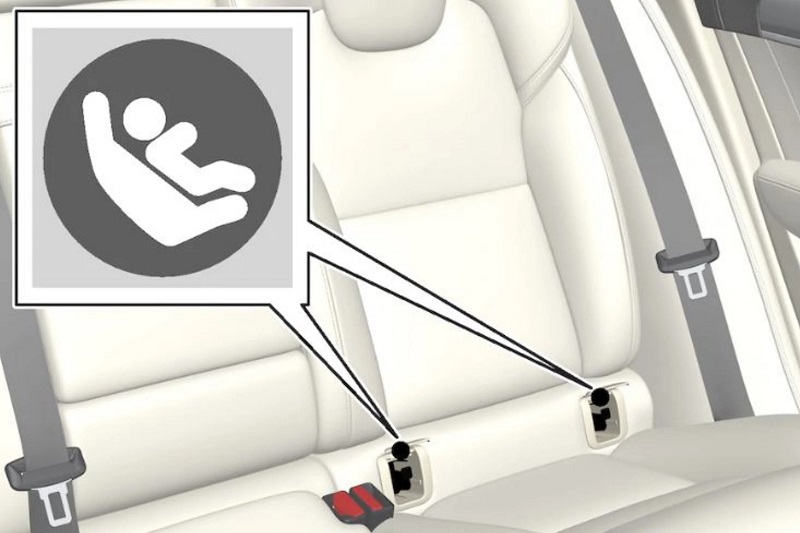

Якірний ремінь (Top Tether)
Ще одна скоба (на додаток до ISOFIX або Latch), яка може розташовуватися за підголовником на задній полиці автомобіля, спинках задніх сидінь, підлозі багажника або на стелі (залежить від марки автомобіля).

Ніжка упору в підлогу
Спеціальне кріплення у вигляді міцної «ноги», яка вбудована в основу автокрісла або спеціальної бази та упирається у підлогу машини.

Головна задача якірного ременя та ніжки упору в підлогу – підвищення надійності кріплення, зменшення навантаження на основні елементи та зниження ризику «ківка» автокрісла у разі різкого гальмування або дорожньо-транспортної пригоди.
3. Матеріали
Зазвичай каркас автокрісла виконаний із пластика, який має бути міцним та витримувати удари. Вторинний пластик може тріскатися і ламатися, тому краще вибрати матеріал первинної обробки. Для комфорту та зручності дитини всі моделі доповнені чохлом із м'яких, приємних на дотик матеріалів. Краще, щоб оббивка була зроблена з натуральних тканин, хоча синтетичні зносостійкіші. За рахунок цього багато виробників комбінують ці матеріали. Важливо, щоб чохол був знімний — його можна легко очистити від забруднень, випрати в пральній машині або навіть замінити. Вітається наявність у комплектації змінних літніх чохлів, спеціальних фартухів проти бруду на спинку переднього сидіння та килимків під автокрісло.
4. Конструкція та ергономіка
Оснащення та конструкція автокрісла впливає не тільки на безпеку, а й на комфорт маленького пасажира. А якщо дитині буде незручно, особливо під час довгих поїздок в автомобілі – істерики, плач, примхи та спроби вибратися неминучі. А це значно відволікає та знижує концентрацію водія, що загрожує ризиком ДТП.
Конструктивні особливості автокрісла в першу чергу залежать від вагової групи. Так, для найменших бажані:
Ремені безпеки (триточкові або п'ятиточкові) – обов'язкова умова для моделей початкових груп, оскільки саме внутрішні ремені автокрісла надійно фіксують і утримують немовля, чого не здатний зробити штатний ремінь (він відповідає за кріплення самого автокрісла). Звичайно, п'ятиточкові ремені надійніші за триточкові, тому що проходять не тільки через плечі і між ніжками, але ще й по талії. Обов'язково звертайте увагу на накладки – вони повинні бути м'якими та не натирати ніжну шкіру дитини.
Анатомічна подушка – спеціальна підкладка, яка додатково забезпечує правильне положення спини, шиї та голови малюка. У кріслах для старших дітей така подушка теж зустрічається, але найчастіше вона виконана у вигляді підголівника для фіксації лише голови.
Ручка для перенесення – дає змогу використовувати автокрісло як люльку-переноску. Це дуже зручно – ви можете переносити сплячого малюка, не порушуючи його сон. Ручки є обов'язковим елементом автокрісел-переносок групи 0+.
Козирок від сонця — маленькій дитині важливий захист від ультрафіолету та сліпучого сонця, а також від дощу, вітру та снігу, якщо автокрісло використовується як переноска.
Накидка на ніжки – чохол, що закриває нижню частину тіла дитини. Актуальний у холодну та вітряну погоду, тому що утеплює та захищає пасажира від опадів (знову ж таки — якщо ви вирішите винести малюка на вулицю).
Якщо говорити загалом про всі групи, корисними будуть такі функції:
Регулювання нахилу спинки – функція, передбачена для дітей, що підросли, оскілки автокрісла для немовлят переважно мають тільки положення напівлежачи. Регулювання спинки дає змогу дитині вибрати максимально комфортне положення, що особливо важливо під час тривалих поїздок – вона може їхати сидячи або подрімати, опустивши спинку.
Бічний захист – додаткові елементи збоку, які захистять дитину та пом'якшать удар у разі ДТП.
Регулювання висоти підголівника – зазвичай використовується в кріслах мультигруп (змішаних вікових груп), тому що дає можливість піднімати підголівник зі зростанням пасажира.
Регулювання ширини спинки – аналогічна функція, що дає змогу підбирати оптимальну ширину спинки з урахуванням віку, ваги та комплекції дитини.
Регулювання висоти ременів також необхідне при перевезенні дітей різного зросту або в міру дорослішання одного пасажира.
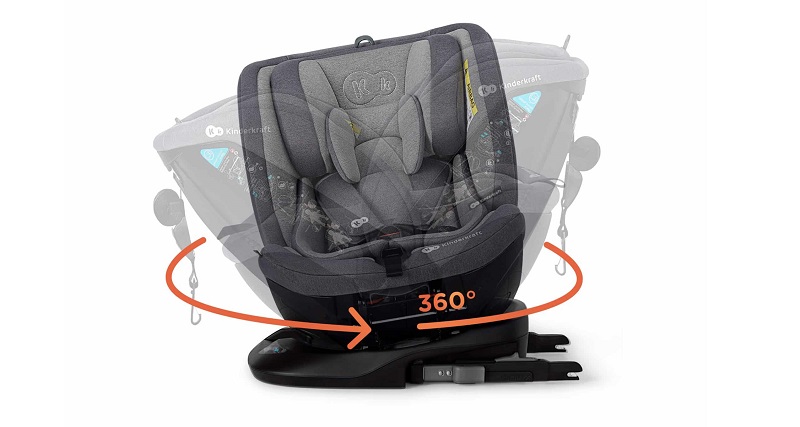
Поворотна система – передбачає наявність нерухомої основи, яка кріпиться до сидіння, і крісла з можливістю повороту в будь-якому напрямку. Це значно полегшує висадку та посадку, а також дає змогу зручно годувати дитину в дорозі. Така система не зустрічається в автокріслах 0+ (тільки якщо це не мультигрупи), тому що немовлят, як ми вже згадували вище, можна перевозити тільки в положенні проти руху.

Знімна спинка – підвищує універсальність автокрісла, тому що дає можливість з часом перетворити його на бустер для дорослої дитини.
Підсклянник – не обов'язковий, але корисний додаток для безпечного утримання пляшечки з напоєм або сумішшю без ризику облити оббивку салону (хоча з активними дітьми такий ризик все ж таки є).
Крім того, автокрісло має бути зручним для батьків. Звертайте увагу на розміри та вагу, щоб пристрій не займав практично все вільне місце в салоні та поміщався у багажник. А враховуючи те, що не завжди поїздка відбувається за участю обох батьків, мамі має бути неважко піднімати автокрісло. Переконайтеся в тому, що процес кріплення та посадки пасажира не займає багато часу і не завдає зайвого клопоту. Зокрема, допоможуть індикатори правильного встановлення.
5. Безпека дитини (стандарти та краш-тести)
Найчастіше «безпека» — це не просто слово, використовуване виробниками для маркетингу, а доведене твердження. Для цього існують спеціальні організації, які перевіряють надійність автокрісла. Тому при покупці не сподівайтеся тільки на запевнення продавців та власні знання, а звертайте увагу на наявність сертифікацій – це прямий доказ того, автокрісло дійсно захистить малюка.
ECE R44 Universal
Європейський стандарт безпеки для дитячих автокрісел, затверджений у 1982 році. З того часу вже вийшло чотири редакції ECE R44: найактуальніший стандарт ECE R44.04 був прийнятий у 2009 році, але можуть експлуатуватись і моделі, що відповідають раннім версіям.
Сертифікат безпеки автокрісла за стандартом ECE R44/04 включає:
- повну комплектацію крісла (фіксатор діагональної лямки, механізм регулювання ременя, докладна інструкція);
- захист від бічних ударів;
- комфортне положення дитини;
- надійність усіх деталей та висока якість матеріалів;
- підказки щодо встановлення крісла на його корпусі.
i-Size
У 2013 році комітетом експертів під егідою Організації Об'єднаних Націй було розроблено новий стандарт під назвою i-Size. Він складається із трьох частин:
- стандарт ECE R129 для автомобільних утримуючих пристроїв (простіше кажучи автокрісел);
- стандарт ECE R16, що регулює вимоги до системи ременів безпеки в автомобілі та вимоги до ISOFIX;
- стандарт ECE R14, який регулює вимоги до якірного кріплення та підлоги автомобіля.
i-Size встановлює більш жорсткі вимоги:
- встановлення крісла проти ходу руху для дітей до 15 місяців (не до 9 місяців);
- Обов'язковий захист при бічному ударі та відповідні випробування (для пасажирів зростом до 105 см);
- Додаткові краш-тести: крісла, сертифіковані за стандартом i-Size, проходять більш строгі краш-тести, включаючи випробування на бічний удар. У випробуваннях використовуються манекени, які точніше імітують анатомію та поведінку тіла дитини при аварії;
- Обов'язкове використання системи ISOFIX;
- Класифікація за зростом а не за вагою дитини.
Сертифіковані крісла мають спеціальні помаранчеві ярлики, на яких вказана наступна інформація:
- номер стандарту безпеки;
- вага (або вага та зріст) пасажира;
- код країни сертифікації («Е» з числом у колі);
- номер краш-тесту.

Поки що обидва стандарти діють паралельно, але згодом ECE 129 i-Size може стати єдиним. Ці стандарти є актуальними для європейських країн.
NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration)
У США діє свій стандарт безпеки – NHTSA, або National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Він менш вимогливий, тому що в Штатах використовують універсальні автокрісла, що підходять дітям різного віку. А самі тести проводять виробники на спеціальних полігонах, тому їхня надійність сумнівна. Європейські стандарти більш строгі, тому не всі системи американського походження допущені до продажу в ЄС.
ANWB, Stiftung Warentest, ADAC
Якщо ж ви хочете більш прискіпливої перевірки на безпеку, є незалежні експертні спільноти та тестувальники: ANWB, Stiftung Warentest, ADAC. Найбільш популярними є краш-тести незалежної громадської організації німецьких автомобілістів ADAC (найбільшої в Європі) – вони вважаються найбільш об'єктивними та строгими. Фахівці ADAC тестують автокрісла на лобовий удар на швидкості 64 км/год, на бічний удар при швидкості 50 км/год та удар ззаду, чого немає у стандартних вимогах. Оцінка від «погано» до «відмінно» дається на конкретну модель, а не на виробника в цілому. При формуванні кінцевої оцінки враховуються такі параметри: безпека, експлуатація, ергономіка, шкідливі речовини та догляд. Таким чином, якщо автокрісло отримало високий бал від ADAC – це справді гарантія безпеки та надійності. До речі, на нашому сайті є спеціальний фільтр за результатами краш-тестів ADAC.
6. Місце для встановлення
Найбільш безпечним вважається центральне заднє сидіння – тут гарний огляд, а у разі зіткнення у дитини є достатня дистанція до місця удару. Але такі сидіння найчастіше маленьких розмірів і не оснащені ременями безпеки чи кріпленнями. Тоді експерти рекомендують ставити автокрісло за пасажирським сидінням – так дитина розміщена з боку тротуару, а не проїжджої частини. Варіанти встановлення за місцем водія або спереду (особливо якщо це автолюлька з немовлям, за яким потрібен контроль) теж популярні.
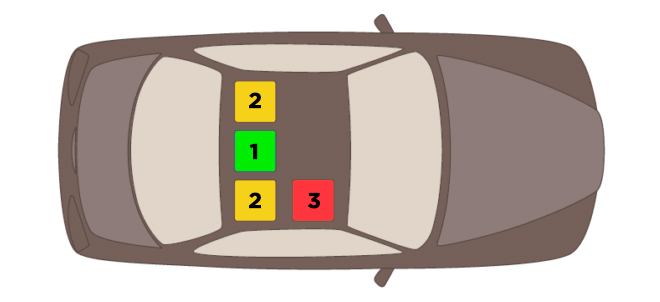
2 – інші рекомендовані місця для встановлення дитячого автокрісла.
3 – можливе місце встановлення за відсутності або вимкненої подушки безпеки.
7. Висновок
На сьогоднішній день на ринку є великий вибір виробників та різних моделей автокрісел, але орієнтуватися варто далеко не на популярність компанії та її «гучне» ім'я. Існує безліч нюансів, які необхідний враховувати при покупці, і ми сподіваємося, що наша стаття допоможе зробити правильний вибір. Найголовніше – ставте на перше місце не бюджет, а безпеку та комфорт дитини: враховуйте відповідність ваговій групі, типи кріплень, якість матеріалів, результати краш-тестів та оснащення.
Бажаємо вам комфортних та безпечних спільних подорожей!
Статті, огляди, корисні поради
Усі матеріали



















































































































































